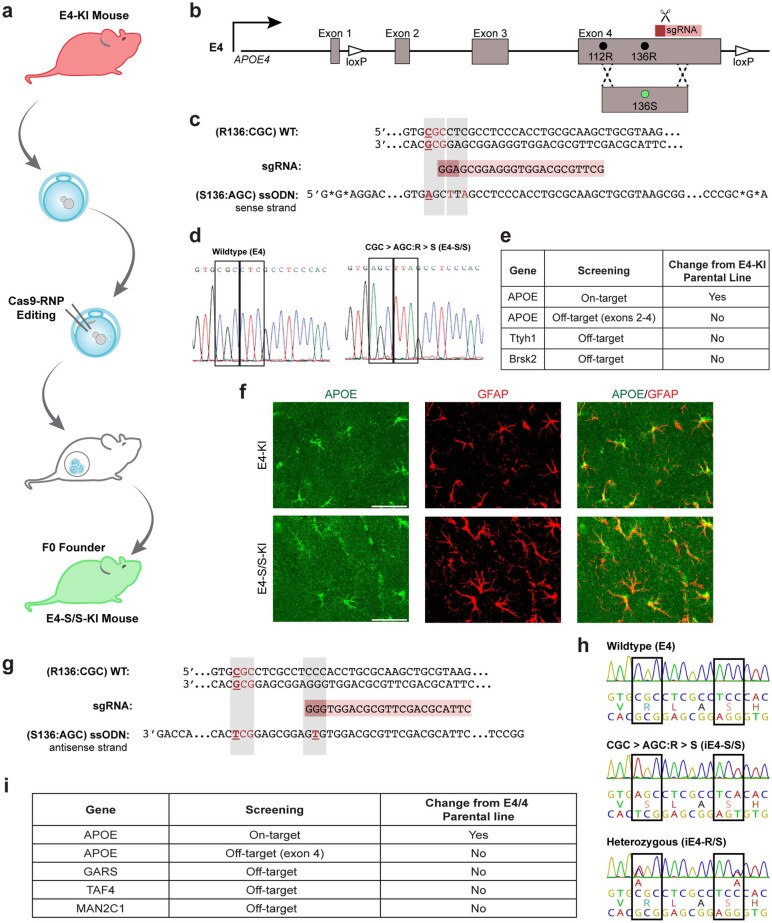
Extended Data Fig. 1. Generation of human APOE4-R136S knock-in mice and APOE4-R136S hiPSC lines by CRISPR/Cas-9-mediated gene editing.
a, Schematic of generating human APOE4-R136S knock-in (E4-S/S-KI) mice using CRISPR/Cas-9-mediated gene editing. b, Schematic of gene editing strategy to generate the R136S mutation in human E4-KI mice (with the loxP sites, unused in current gene-editing strategy) and to generate APOE4-R136S (E4-S/S) hiPSC lines (without the loxP sites). c, DNA sequences of WT human APOE4 loci encoding for R136, designed sgRNA, and single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides donor repair template encoding for S136 and silent mutation at PAM site for generating E4-S/S-KI mice. d, Sanger DNA sequencing of WT APOE4 and APOE4-S/S at and near the site encoding for residue 136 in E4-S/S-KI mice. e, Summary of on-target R136S editing in APOE4 and potential off-target mutation screening for knock-in mice. f, Representative immunofluorescent images of APOE (green) and GFAP (red) in CA1 hippocampal subfield in E4-KI and E4-S/S-KI mice at 12 months of age (scale bar, 50 μm). g, DNA sequences of WT APOE4 loci encoding for R136, designed sgRNA, and single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides donor repair template encoding for S136 and silent mutation at PAM site for generating E4-S/S hiPSC lines. h, Sanger DNA sequencing of WT E4, E4-S/S, and E4-R/S at and near the site encoding for residue 136 in hiPSC lines. i, Summary of on-target R136S editing in APOE4 and potential off-target mutation screening in hiPSC lines. Experiments depicted in representative images in f were performed on n = 3 mice per genotype using 2 brain sections per mouse, with reproducible data. WT, wildtype; sgRNA, single guide RNA; ssODN, single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide.