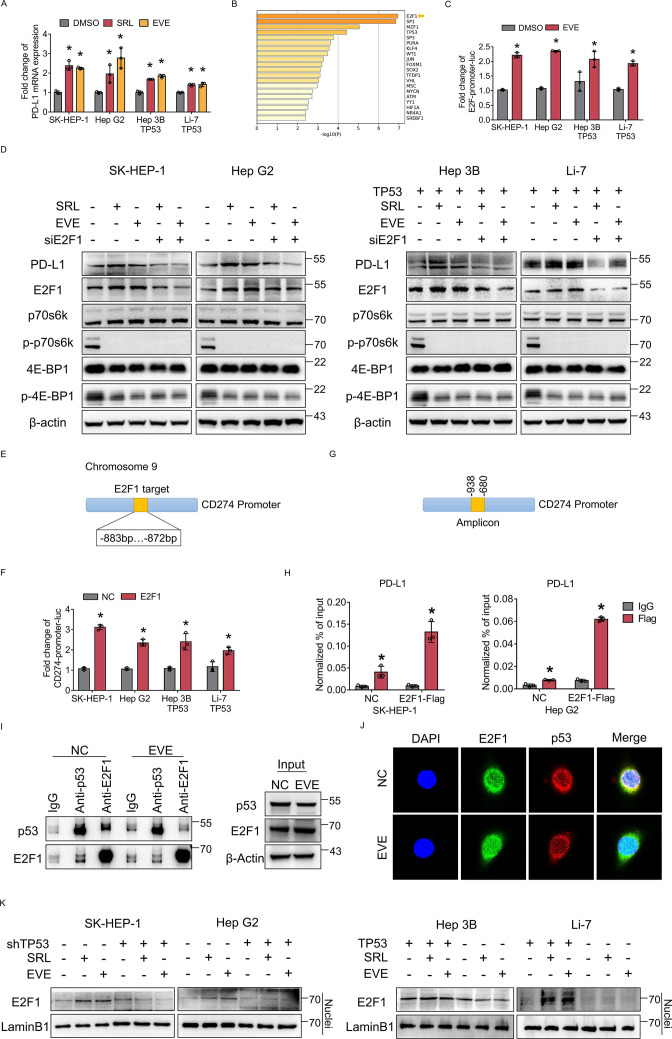
Figure 3.
E2F1 promotes PD-L1 transcription after mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 suppression in p53 wild-type HCC cells. (A) TP53 wild-type cells (SK-HEP-1, HepG2) and TP53 loss-of-function cells (Hep3B, Li-7) with TP53 overexpression were treated with everolimus or sirolimus. PD-L1 mRNA expression was detected by qRT-PCR. (B) ATAC-seq analysis of TP53 wild-type cells treated with SRL. (C) The fold change in the relative luciferase activity was examined in HCC cells treated with everolimus. (D) SK-HEP-1, HepG2, Hep3B (TP53 overexpression), Li-7 (TP53 overexpression) with or without E2F1 knockdown were treated with everolimus or sirolimus. The protein level of PD-L1, E2F1, p70s6k, p-p70s6k, 4E-BP1 and p-4E-BP1 were detected using western blotting. β-actin was used as the loading control. (E) Predicted E2F1 binding site sequences in the PD-L1 promoter. (F) The fold change in the relative luciferase activity was examined in HCC cells transfected with E2F1 plasmids (E2F1) or empty plasmids (NC). (G) Amplicons in the CD274 promoter were used for ChIP assay (H) which was performed to determine the binding of E2F1 to the binding site sequence of the CD274 promoter in SK-HEP-1 and HepG2 cells transfected with E2F1 plasmids (E2F1) or empty plasmids (NC). (I) The interaction of endogenous p53 and E2F1 was tested in HCC cells treated with or without everolimus. Normal rabbit IgG was used as a control. (J) Colocalization (yellow) of E2F1 (green) with p53 (red) by confocal microscopy. The nuclei were stained with DAPI. (K) Nuclear proteins were isolated and subjected to western blotting for expression of E2F1. LaminB1 was used as the loading control. *p<0.05, compared with the DMSO (A, C) or NC (F) or IgG (H) groups. ACTC-seq, assay for transposase accessible chromatin; CD274, cluster of differentiation 274; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; DAPI, 4,6-diamino-2-phenyl indole; DMSO, Dimethylsulfoxide; EVE, everolimus; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; mRNA, messenger RNA; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; RT-qPCR, Real Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction; SRL, sirolimus.