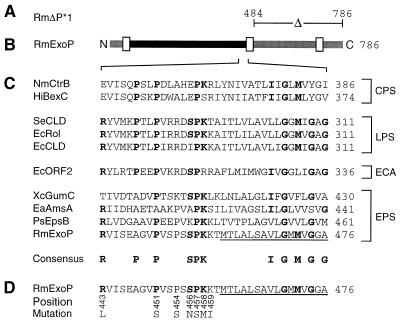
FIG. 2.
Characteristic features of different R. meliloti ExoP mutant proteins. (A) The part deleted in the ExoP protein encoded by the exoP* gene of mutant RmΔP*1 (6) is indicated. (B) Linear scheme of the R. meliloti wild-type ExoP protein. Putative transmembrane or membrane-associated segments (6) are marked by white boxes. Parts of ExoP probably located in the periplasm and the cytoplasm are indicated in black and grey, respectively. (C) Alignment of partial sequences of ExoP and similar proteins involved in the biosynthesis of capsular polysaccharides (CPS), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), entobacterial common antigen (ECA), and exopolysaccharides (EPS). Residues identical in at least four proteins of three different groups are printed in bold letters and are included in the consensus sequence. (D) Single substitutions of amino acid residues of the ExoP protein. Numbers below the partial ExoP sequence indicate the positions of the amino acid residues replaced by the residues indicated. Amino acid residues of the ExoP protein which are probably part of a membrane spanning helix are underlined. Numbers to the right indicate amino acid positions. Abbreviations: PsEpsB, Pseudomonas solanacearum EpsB (23); EaAmsA, Erwinia amylovora AmsA (11); EcCLD, E. coli O111 CLD (2); EcORF2, E. coli K-12 ORF2 protein (27); EcRol, E. coli O75 Rol (3); HiBexC, Haemophilus influenzae BexC (24); NmCtrB, Neisseria meningitidis CtrB (18); SeCLD, Salmonella enterica LT2 CLD; RmExoP, R. meliloti ExoP (5); XcGumC, Xanthomonas campestris GumC (6, 13).