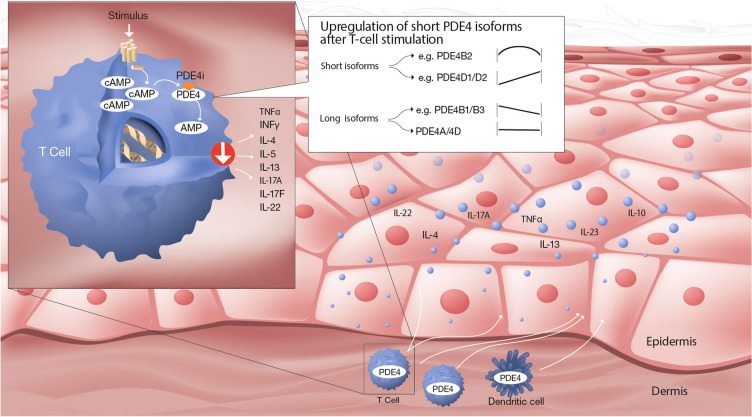
Fig. 2.
Schematic illustration of the regulation of PDE4 isoforms in stimulated T cells and the importance of inhibiting short isoforms to prevent production of inflammatory cytokines in skin. The figure is based on PDE4 isoform data obtained using anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation of CD4+ T cells [10]. The key findings were as follows: (i) The upregulation of short PDE4 splice variants was reported to account for the induction of PDE4 activity in stimulated CD4+ T cells; (ii) PDE4B2 was transiently upregulated; (iii) PDE4D1/D2 were upregulated in a time-dependent manner; (iv) PDE4B1/B3 were downregulated over time; (v) Long PDE4A/4D isoforms were unchanged; and (vi) Short isoforms of PDE4A/PDE4C and long isoforms of PDE4C were not detected. Inhibition of PDE4B2 and PDE4D1/D2 leads to increased levels of cAMP and reduced levels of disease driving cytokines in the skin
The figure was created with assistance from Erik Nylund, VisualizeThat AB