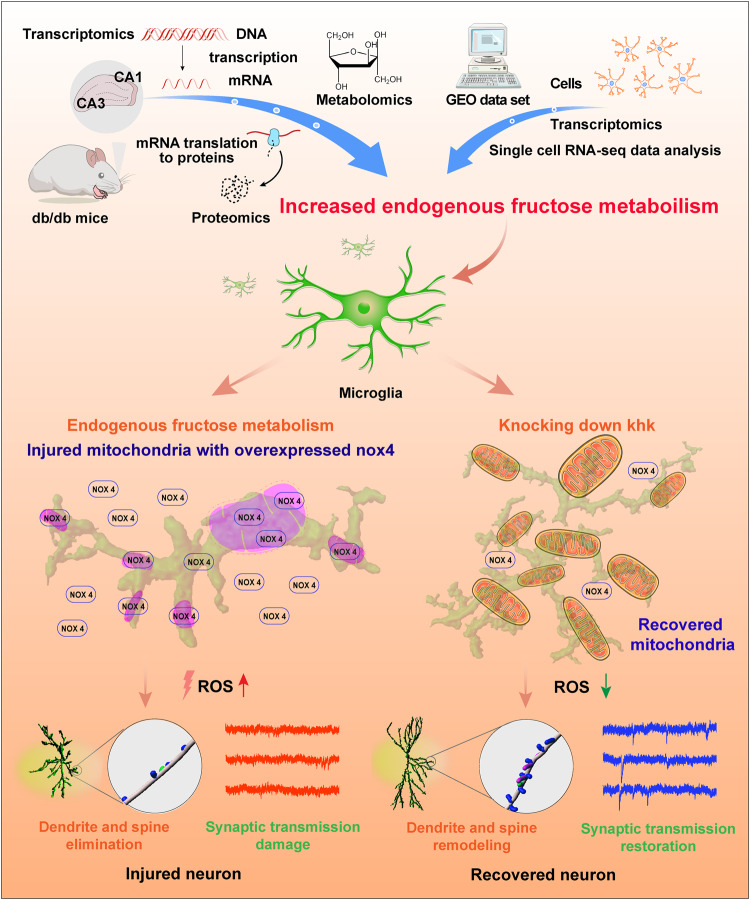
Fig. 8. Graphic summary illustration.
Multiomics analysis of the mouse hippocampus demonstrated that endogenous fructose metabolism was increased in T2DM animals. Further experiments illustrate that endogenous fructose metabolism occurs predominantly in microglia of the hippocampus and is boosted during T2 diabetes mellitus, leading to the overexpression and mitochondrial translocation of NOX4. Translocated NOX4 injures mitochondria and consequently destroys microglial redox hemostasis. Overproduction of ROS from microglia mediates synaptic deficits and promotes the development of DACD. Knocking down Khk downregulates NOX4 expression and mitochondrial translocation and reduces ROS generation in microglia, which in turn restores synaptic impairment and alleviates DACD.