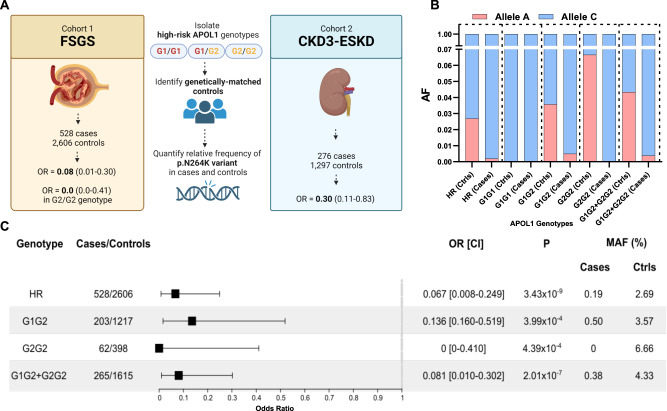
Fig. 1. Protective effect of the APOL1 p.N264K missense variant against G2-associated FSGS.
A Graphical representation of the study design, cohorts and main results of the study. Stratified association analysis of the combined cohort of 528 APOL1 high-risk FSGS and 2606 genetically-matched APOL1 high-risk controls: B stacked bar plot for the p.N264K MAF across APOL1-HR genotypes in cases and controls; the Allele C is the reference allele encoding for the p.N264; the Allele A is the minor allele resulting the p.K264 variant amino acid; C Forest plot for the p.N264K association analysis showing significantly protective odds ratios across APOL1 high risk (G1G1, G2G2 and G1G2) genotypes. The plot describes odd ratio and confidence interval for HR (OR = 0.067), G1G2 (OR = 0.136), G2G2 (OR = 0) and G1G2 + G2G2 (OR = 0.081). The P values were obtained separately for aforementioned individual risk alleles using two sided Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel chi-squared test without multiple correction across the alleles (See Methods). No OR or CI for the G1G1 genotype (263 cases, 991 controls) are shown in forest plot because the p.N264K was absent in both groups (the APOL1 G1 and p.N264K alleles are mutually exclusive), resulting in undefined OR, infinite CI, and a p-value of 1. FSGS focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, CKD chronic kidney disease, ESKD end-stage kidney disease, AF allele frequency, Ctrls controls, OR odds ratio, CI = 95% confidence interval, MAF minor allele frequency. The cartoon in (A) has been created using BioRender at www.biorender.com.