Fig. 3. Plasticity among Tc subsets.
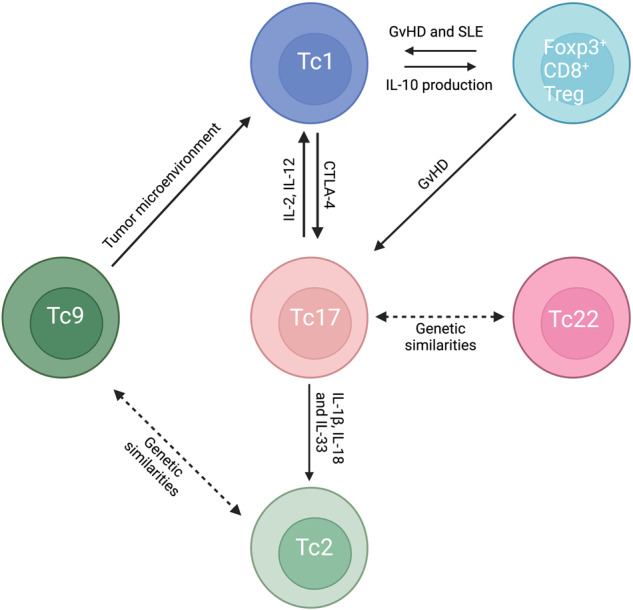
Tc17 cells, akin to Th17 cells, display high plasticity in terms of cytokine production under specific conditions, and conversely, other Tc subsets can transform into Tc17 cells within certain contexts. Adoptive transfer of in vitro differentiated Tc17 cells led to their production of IFN-γ and granzyme B, similar to Tc1 cells. CTLA-4 plays a role in shifting the programming of Tc1 cells toward Tc17 cell differentiation. In the skin, alarmins such as IL-1, IL-18, and IL-33 stimulate commensal bacteria-specific Tc17 cells to produce Tc2 cytokines. Tc17 cells and Tc22 cells exhibit shared features, including similar differentiation-inducing cytokines, signaling transcription factors and cytokine production profiles. In a GvHD model, some adoptively transferred Foxp3+CD8+ Tregs were transformed into Tc17 and Tc1 cells. In addition to Tc17 cells, constituting another Tc subset also exhibit plasticity. Tc1 cells can produce IL-10 and exhibit suppressive functions in the context of viral infection. Tc2 and Tc9 cells share common features, including differentiation-inducing cytokines, signaling transcription factors and cytokine production profiles. In the tumor microenvironment, Tc9 cells undergo conversion to Tc1 cells, leading to potent antitumor immune responses, whereas Tc2 cells do not significantly contribute to attenuated tumor development.
