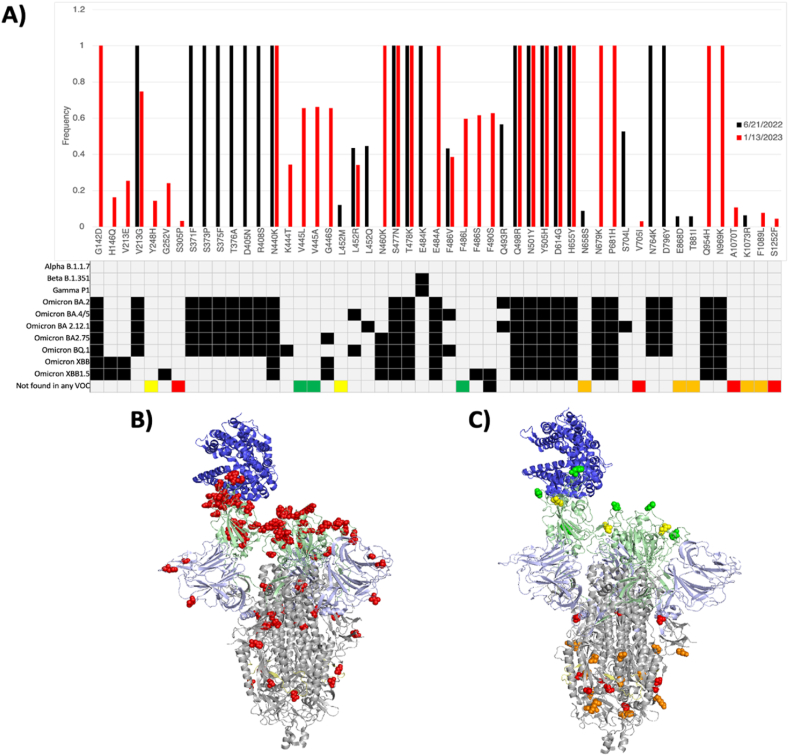
Fig. 7.
Whole genome sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 S gene from wastewater. SARS-CoV-2 RNA extracted from wastewater was sequenced on 6/21/22 and 1/13/23. (A) Each mutation and its frequency on 6/21/22 (black) and 1/13/23 (red) were plotted. For each mutation, grey boxes designate variants of concern that do not contain the mutation and black boxes represent variants of concern that do contain the mutation. Colored boxes in the last row designate mutations that are not found in any variant of concern. The color of the box designates the frequency of the mutation, with red referring to 0–5%, orange 5–10 %, yellow 10–50 %, and green >50 %. The SARS-CoV-2 S protein contains multiple domains, including the receptor binding domain (light green), furin cleavage site (light yellow), and N-Terminal Domain (light blue) and the receptor binding domain (light green), which binds to the ACE-2 (dark blue) cellular receptor. Known (B) and novel (C) mutations were plotted as red spheres on the S protein structure, with novel mutations being color-coded based on their frequency, with red referring to 0–5%, orange 5–10 %, yellow 10–50 %, and green >50 %. SARS-CoV-2 S protein structures were created by PyMol.