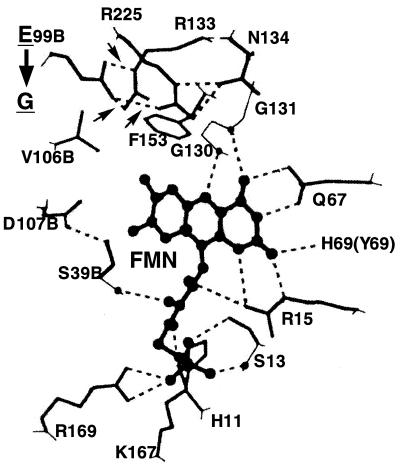
FIG. 2.
Disruption of presumed hydrogen bonds in the active center of NfsA by a Glu-to-Gly substitution at position 99. Sixteen of 17 amino acids surrounding the FMN cofactor are invariant between Frp and NfsA, strongly suggesting that the three-dimensional structure of NfsA is very similar to that of Frp. We presume the active center of NfsA to possess a hydrogen-bonding pattern virtually identical to that of Frp (10). Thus, this figure is adapted from Tanner et al. (10). As with Frp Glu-99, NfsA Glu-99 has hydrogen bonds with Arg-225 and Arg-133. These hydrogen bonds, which are labeled with three small arrows, are disrupted by the Glu-to-Gly substitution (see the thick vertical arrow) so that the structurally relaxed active center of the mutant NfsA can accommodate large molecules such as FMN as substrates. Invariant amino acids surrounding or forming the active center are His-11, Ser-13, Arg-15, Ser-39, Gln-67, Glu-99, Val-106, Asp-107, Gly-130, Gly-131, Arg-133, Asn-134, Phe-153, Lys-167, Arg-169, and Arg-225. Tyr-69 of Frp (in parentheses) is replaced by His-69 in NfsA. Residues marked with B are from the other subunit.