Figure 1.
Stx3-dependent postsynaptic membrane fusion in CA1 is critical for novelty preference and reward anticipation.
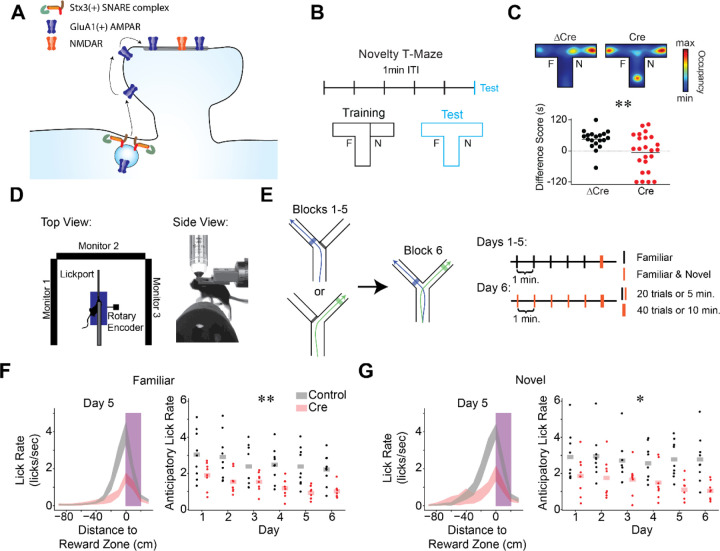
A) Model of Stx3-dependent AMPA receptor trafficking. Stx3(+) SNARE complexes insert GluA1(+) AMPA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane adjacent to spines in an activity dependent manner. Receptors laterally diffuse into the synapse, leading to potentiation.
B-C) CA1 Stx3 is necessary for novel environment preference
B) Novel environment preference assay. During training trials, animals can explore one arm of a T-maze (familiar arm “F”), while the other arm is blocked (novel arm, “N”). During the test trial, the block is removed and animals are free to explore the full maze. ITI - inter-trial-interval.
C) CA1 Stx3 is necessary for novel environment preference. Top - Representative test trial from a single Cre-injected and a single ΔCre mouse. Heatmaps indicate relative occupancy of each location. Bottom - Novel arm preference score [difference score = (time spent in the novel arm) - (time spent in the familiar arm)]. Dotted line indicates equal time spent in the two arms [N=19 control mice, 24 Cre mice. Unpaired t-test: t=2.83, p=0.007]
D) Schematic of the head-fixed virtual reality (VR) and two photon (2P) apparatus.
E) Task design of the VR novel arm Y-Maze. Left - Track schematic. Arrows indicate the animals’ trajectory on left or right trials. Shaded regions indicate reward zones. Right - Training protocol. Days 1–5: 5 blocks of “familiar arm” trials (20 trials or 5 minutes, black), 1 block of randomly interleaved “familiar” and “novel arm” trials (40 trials or 10 minutes, orange). Animals are forced to take left or right trajectories on each trial. The animals cannot control the yaw angle in the virtual environment. Day 6: familiar and novel arms randomly interleaved in all blocks.
F-G) CA1 Stx3 is necessary for reward anticipation behaviors.
F) Control animals (gray) display more anticipatory licking than Cre-injected animals (red). Left - peri-reward lick rate on familiar arm trials as a function of position relative to the reward zone on day 5 (magenta - reward zone, shaded regions indicate across animal mean ± sem). Right - Average familiar trial peri-reward lick rate on each day. Dots indicate the across trial average for each mouse. Shaded bars indicate across animal mean. [N=9 control mice, 8 Cre mice, 6 days. Mixed effects ANOVA: virus main effect F(1,15)=10.66 p=5.22×10−4, day main effect F(5,75)=7.55 p=8.61×10−6, interaction F(5,75)=.801 p=.55].
G) Same as (F) for novel arm trials. [N=9 control mice, 7 Cre mice, 6 days. Mixed effects ANOVA: virus main effect F(1,15)=8.40 p=.011, day main effect F(5,75)=2.01 p=.087, interaction F(5,75)=1.33 p=.263]
See also Figures S1 & S2.