Figure 4: Biofilm rescue by DvhD is c-di-GMP dependent.
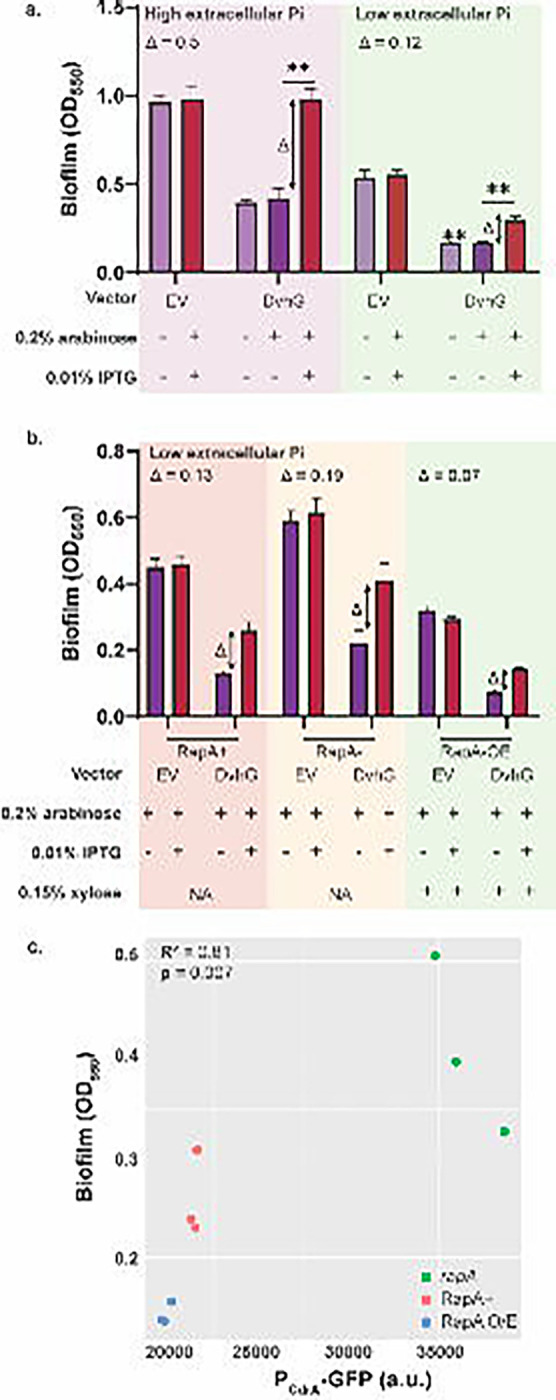
a) Biofilm formed in the Pf0-1 attTn7::lacIPtacdvhD-HA ΔlapGΔlapDdvhA-hlx-swap strain in low phosphate K10Tπ medium (~0.14 mM) or high phosphate K10T medium (1 mM) at 24 hours. The strain contains either no vector, an empty vector or a plasmid expressing full length DvhG. Arabinose at 0.2% concentration and IPTG at 0.01% concentration are used to induce dvhG expression from the plasmid and dvhD expression from the genome, respectively. “Δ” quantifies the extent of biofilm rescue by DvhD and is represented by the difference in biofilm formation by the strain expressing DvhG but not DvhD (purple bar) and biofilm formation by the strain expressing both DvhG and DvhD (red bar). b) Biofilm formed by the Pf0-1 attTn7::lacIPtacdvhD-HAΔlapGΔlapDdvhA-hlx-swap strain in low phosphate K10Tπ medium at 24 hours with, active phosphodiesterase RapA (RapA+), without RapA (ΔrapA) or with RapA overexpressed by xylose-inducible PxutR promoter (RapA OE) in the background. The extent of biofilm rescue by DvhD “Δ” is compared among the three strains and indicated over the bar plots. Statistical analysis was performed using one way ANOVA test (ns, p > 0.05; *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001; ****, p ≤ 0.0001). c) Graph representing intracellular c-di-GMP levels calculated from GFP fluorescence from a PCdrA-gfp promoter transcriptional fusion plotted versus biofilm formed when DvhD is induced. Linear correlation (R2) and statistical significance was calculated using Pearson’s test in R (v 4.3.0).
