Figure 6. Transcription inhibition with triptolide restores fork resection in RNase H2‐depleted HeLa cells.
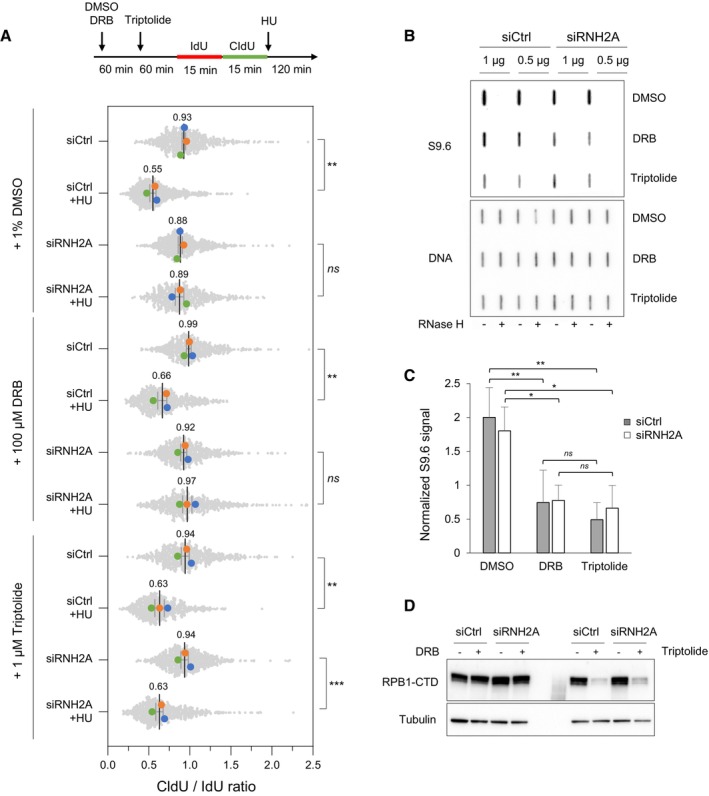
- Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 48 h and were treated with DMSO, 100 μM DRB or 1 μM triptolide for indicated time periods. Cells were labeled with two pulses of IdU and CldU for 15 min before the addition of 4 mM HU for 2 h. RNA polymerase II inhibitors were present during HU treatment. Fork resection was analyzed by DNA fiber spreading and the ratio of CldU to IdU track (~100–300 tracks/condition) length was determined in three independent experiments. Mean (n = 3) and SEM are indicated. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, non‐significant, paired t test.
- HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA and treated with RNAPII inhibitors as indicated in panel A, but without HU treatment. Total genomic DNA was extracted and treated as described in Materials and Methods. RNA:DNA hybrids were detected using the S9.6 antibody and RNase H‐treated samples were included as controls. Double‐stranded DNA was used as loading control. A representative image of four independent experiments is shown.
- Intensity of S9.6 signal in cells treated as indicated in panel (B), normalized to total DNA. Mean and SEM are shown (n = 4 biological replicates). ns P > 0.05; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, two‐way ANOVA.
- HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA and treated with RNAPII inhibitors as indicated in panel (B). RNAPII was detected by immunoblotting using an antibody against the C‐terminal domain of the Rpb1 subunit. Tubulin was used as a loading control.
Source data are available online for this figure.
