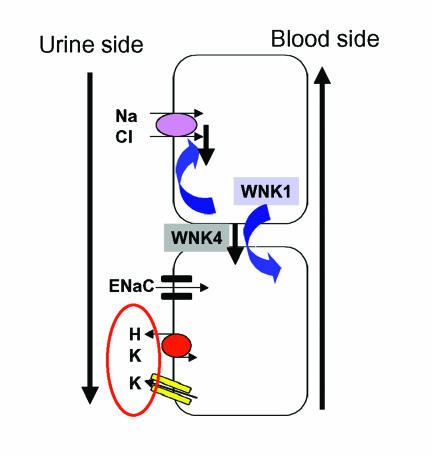
Figure 4.
Shown is the distal nephron. The thiazide-sensitive Na, Cl cotransporter is over-active in pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2. As a result, less Na is available for the ENaC and less K and H ions are excreted in the cortical collecting duct. Therefore, the syndrome features volume expansion, hypertension, hyperkalemia and mild hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. “With-no-lysine” (WNK) kinase 4 down-regulates the cotransporter. When the kinase is mutated, the cotransporter is hyperactive. WNK1 regulates WNK4 downward. Gain-of-function mutations in WNK1, would downregulate WNK4, causing cotransporter hyperactivity.