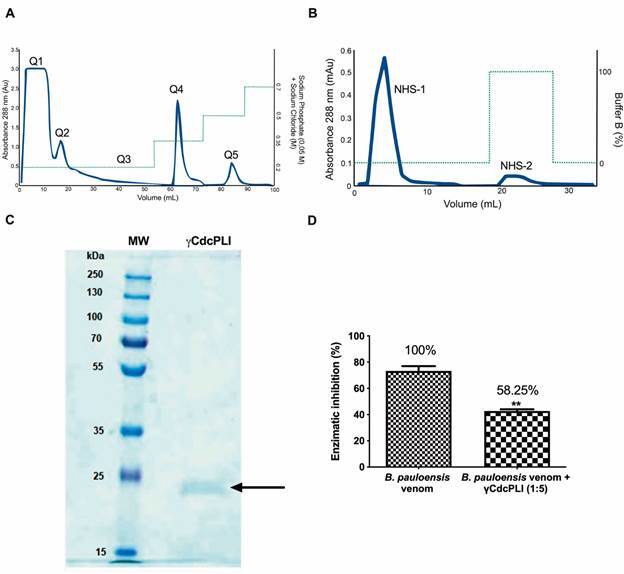
Fig. 1: isolation of γCdcPLI from Crotalus durissus collilineatus snake serum. (A) 98 mg of lyophilised serum was dissolved in 1 mL of 0.05 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) containing 0.2 M NaCl, applied to ion exchange chromatography (Q-Sepharose), equilibrated and eluted with buffer 0.05 M sodium phosphate with different NaCl concentrations (0.2, 0.35, 0.5 and 0.7 M) at a flow rate of 12 mL/h 25ºC. (B) NHS-Hitrap affinity chromatography (N- hydroxysuccinimide) coupled with BnSP-7 of Q4 fraction (8.7 mg) in (Buffer A: 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.5; Buffer B: 100 mM glycine-HCl buffer, pH 2.0). (C) 12.5% (w/v) sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of γCdcPLI: MW: molecular weight markers (250, 130, 100, 70, 55, 35, 25 and 15 kDa). The black arrow indicates the isolated protein. (D) Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity inhibition (Bothrops pauloensis venom: γCdcPLI, 1:5; w/w). NHS-2 fraction (0.5 mg) contains the γCdcPLI inhibitor, according to Gimenes et al. 27 . Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Significant differences were determined using Unpaired Student’s t test (two-tailed). Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05.