Fig. 3.
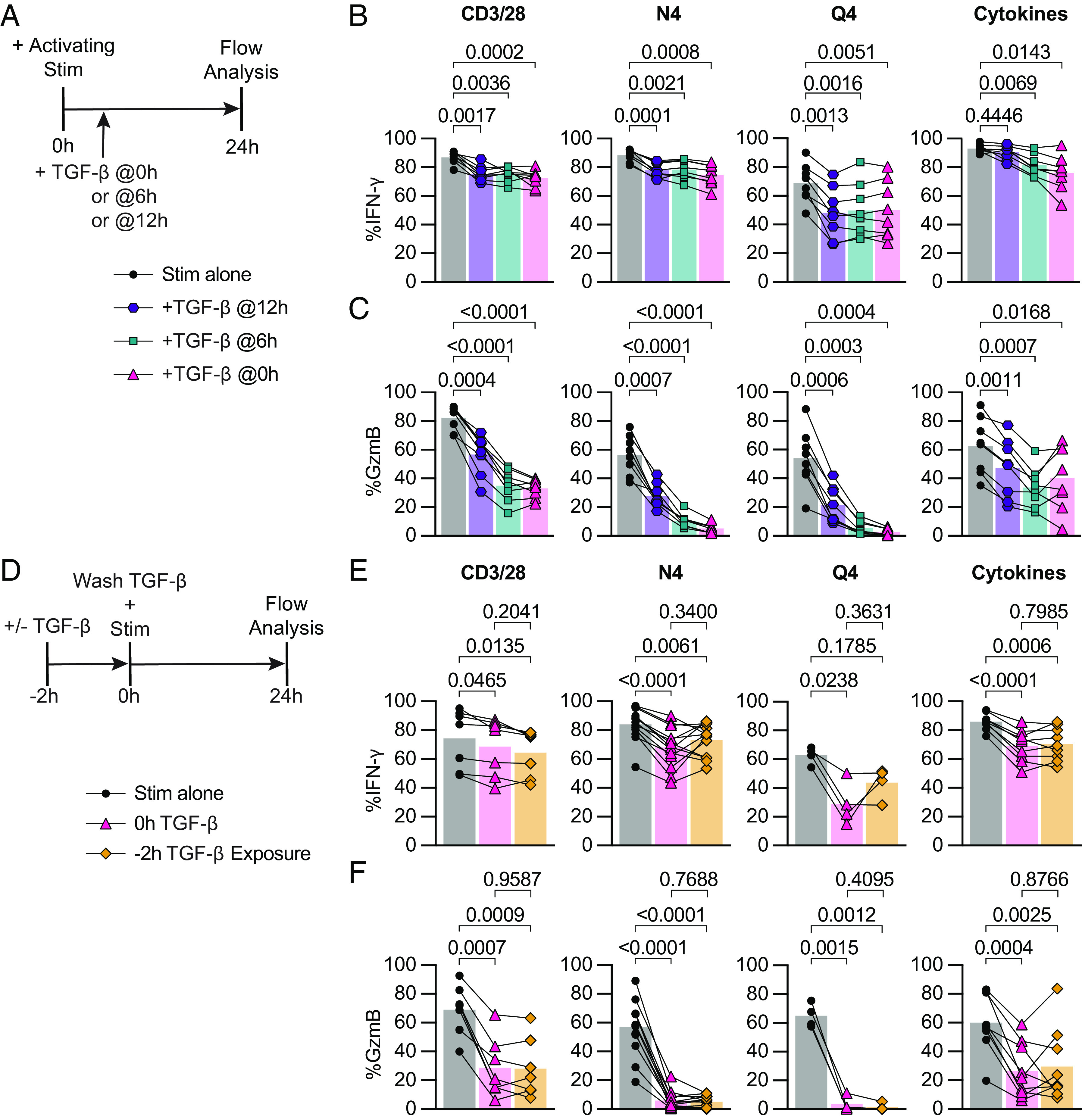
TGF-β inhibits cytotoxicity from recently reactivated memory CD8+ T cells, and short-term exposure to TGF-β inhibits cytotoxicity of subsequently activated memory CD8+ T cells. (A) Schematic of ex vivo stimulation; cells were stimulated for 24 h with CD3/28, N4, Q4, Cyt, and TGF-β at 100 ng/mL. TGF-β was added 0 h, 6 h, or 12 h poststart of activating stimulation. (B) Frequencies of IFN-γ and (C) GzmB in OT-I Tmem compared across stimulation conditions with TGF-β addition at indicated time points (n = 8 animals). (D) Schematic of ex vivo stimulation of isolated T cells from OT-I memory mice. Cells were treated with 100 ng/mL TGF-β or media alone for 2 h, the TGF-β was then washed out (down to 0.001 ng/mL), immediately followed by 24 h of activating stimulation. Stimulations were CD3/28, N4, Q4, Cyt, and TGF-β at 100 ng/mL. (E) Frequencies of IFN-γ and (F) GzmB in OT-I T cells compared across stimulation conditions. CD3/28 data depicted are from n = 7 animals, N4 from n = 13, Q4 from n = 4, and Cyt from n = 9. All indicated statistical significances were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Data shown are from 3 to 10 independent experiments.
