Fig. 4.
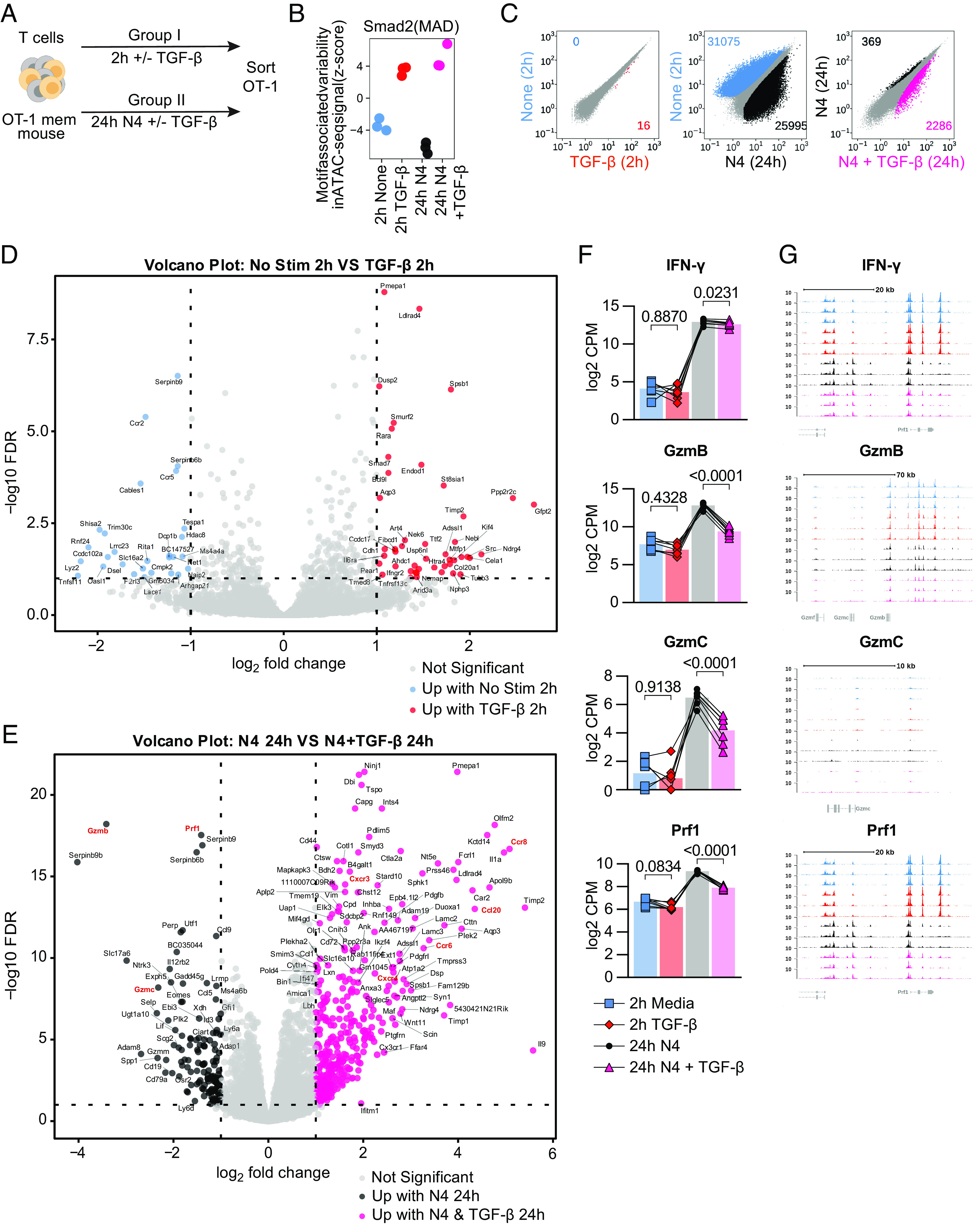
TGF-β epigenetically and transcriptionally alters memory CD8 T cell function. (A) Schematic for T cell isolation with MACS from Ag-experienced OT-I memory mice, subsequent ex vivo stimulation, and sorting of Live, CD8+, CD45.1+ OT-I Tmem cells. Sorted OT-I Tmem were processed immediately for ATAC- and RNA- seq library preparation and sequencing. Stimulations were 2 h with media alone or TGF-β at 100 ng/mL and 24 h 100 nM N4 with or without TGF-β at 100 ng/mL. (B) chromVAR analysis of ATAC-seq signal (z-score) with SMAD transcription factor motifs. The colors are indicative of the experimental condition and also used in C. (C) Scatterplots comparing differentially accessible chromatin regions for pairs of stimulation conditions (from left to right): 2 h untreated vs. 2 h + TGF-β; 2 h untreated vs. 24 h reactivated; 24 h reactivated vs. 24 h reactivated + TGF-β. Plots compare the normalized signal in counts/per peak at all regions across the genome to identify individual peaks that meet the criteria for differential accessibility based (at least 1.5-fold estimated change and adjusted P value of less than 0.01). The number of differentially accessible peaks is shown for each condition in each plot. (D) Volcano plot depicting differentially expressed genes between 2-h media and (E) Twenty-four-hour 100 ng/mL N4 stimulation conditions: with TGF-β or without TGF-β. DE gene cutoff values were adj P value 0.1, Log FC > 1 and < −1. (F) Selected DE genes from RNAseq and indicated statistical significance. (G) Chromatin accessibility of selected genes from ATAC-seq. All data depicted are from n = 7 animals and 2 independent experiments.
