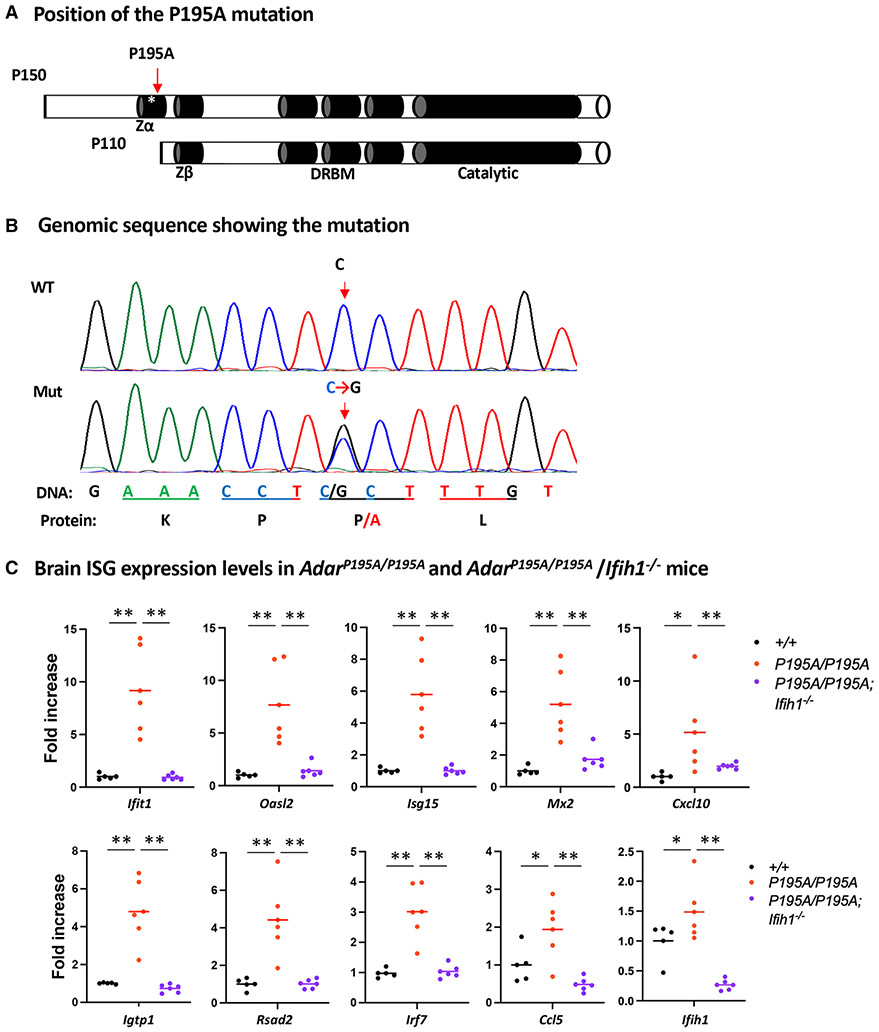
Figure 1. ADAR1 P195A mutation activates MDA5-dependent ISG expression in mouse brains.
(A) Two isoforms of ADAR1, p150 and p110, are expressed from the Adar1 gene. The p150 isoform contains the Zα domain at the N terminus; the Zβ domain, which is not known to bind nucleic acids, the three dsRNA-binding motifs (DRBMs), and the catalytic domain in the C terminus are shared by p150 and p110 isoforms. The asterisk marks the P195A site in the Zα domain; the Zα domain is not present in the p110 isoform.
(B) Mouse genomic sequences flanking the mutation site were confirmed using Sanger sequencing analysis. A single C>G nucleotide replacement that codes the P195A mutation is shown on the sequence histography indicated by the arrows, and the corresponding protein sequence is shown at the bottom.
(C) Mouse brain ISG expression was assessed at mRNA levels. Expression of a panel of 10 selected ISGs was measured using real-time RT-PCR, and the ISG expression levels in AdarP195A/P195A mice (n = 6) were compared with those of WT control (n = 5) and AdarP195A/P195A; Ifih1−/− mice (n = 6). Each dot shows the ISG level of a mouse, and the bars represent the means. The nonparametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to test the differences between the two groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.