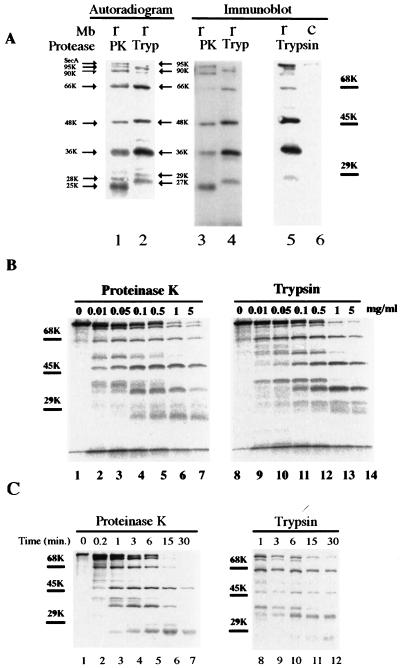
FIG. 1.
Proteolysis of membrane-integrated SecA with proteinase K and trypsin. (A) 35S-labeled SecA fragments in membranes generated by proteolysis with proteinase K or trypsin. Reconstituted membranes (r) or SecA-depleted control membranes (c) from CK1801.4 were subjected to protein translocation reaction and proteolysis as described in Materials and Methods. The resulting SecA fragments in the membrane fraction were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography (lanes 1 and 2) or by immunoblotting using anti-SecA antibodies (lanes 3 to 6). Lanes 1 and 2 and lanes 3 and 4 were from the same gel but were developed differently. The positions of the molecular-marker proteins bovine serum albumin (68 kDa), ovalbumin (45 kDa), and carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa) are shown by bars. The sizes of the protease-resistant SecA fragments are indicated by arrows. (B) Proteolysis of membrane-associated SecA with proteinase K or trypsin was carried out as for panel A, except that the different protease concentrations indicated were used. (C) Kinetics of proteolysis of membrane-integrated 35S-labeled SecA. Proteolysis was performed as for panel A except that the incubation was carried out for the times indicated.