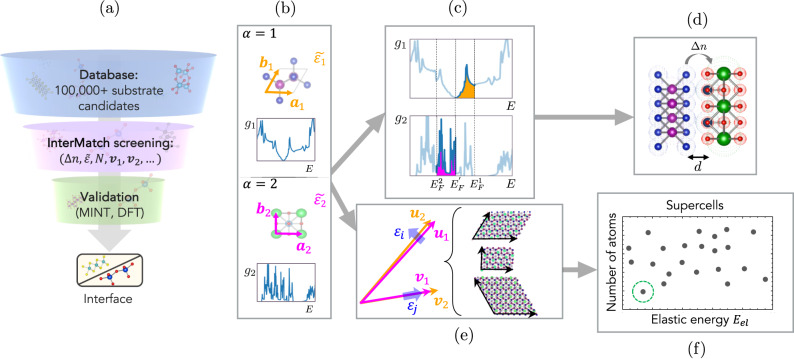
Fig. 1. Role of InterMatch and algorithm overview.
a Role of InterMatch in the materials discovery process. After materials' data are queried from major existing materials databases, InterMatch performs pairwise high-throughput screening calculations of interfacial properties, producing output that can be used as input for ab initio verification of the optimized interface candidates. b Input from the bulk database. Lattice vectors , , density-of-states gα, and elastic tensors of systems α = 1, 2, shown in the top and bottom subpanels, respectively. c are bulk Fermi levels and is new equilibrium Fermi level. d Δn is the transferred charge density and d is the interlayer separation between the two systems, taken to be the sum of the largest van der Waals radii of the species in each system 1 and 2. e Superlattice vectors (left) and candidate supercells (right). Superlattice vectors vi (orange arrows) and their near-equivalent vectors ui (magenta arrows). Candidate supercells, formed in each basis by combining {(vi, ui), (vj, uj)} pairs specify the strain εi (blue arrows). f Optimal supercell minimizes the elastic energy and the number of atoms in the cell. d, f These are the outputs of the InterMatch program.