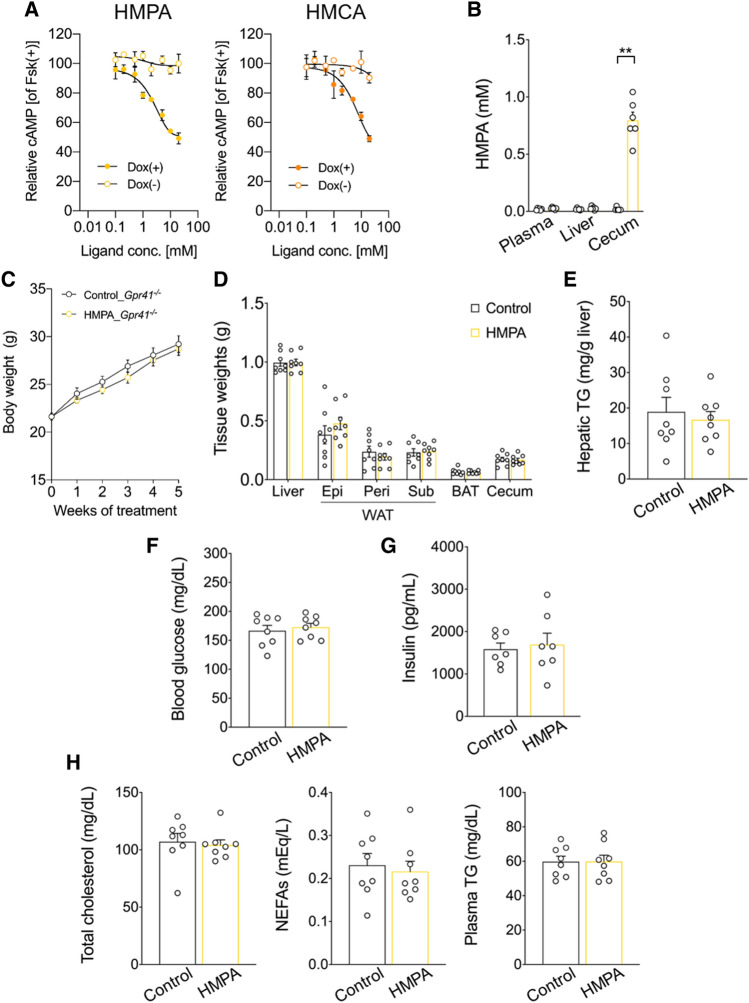
Figure 3.
Affinity of HMPA for GPR41 and HMPA-mediated metabolic effects via GPR41. (A) cAMP inhibition assay for HMPA or HMCA using mouse-GPR41-expressing HEK293 cells. Cells were cultured for 24 h and then treated with or without 10 μg/mL of doxycycline (Dox) (n = 6 independent cultures). All data are presented as relative to forskolin (Fsk)-induced cAMP levels. Closed symbols represent values from cells treated with Dox, and open symbols denote untreated groups. (B) Gpr41−/− male mice were fed HFD containing 1% HMPA for 5 weeks. HMPA contents among plasma, liver, and cecum (n = 6 per group). (C) Bodyweight gain during HMPA treatment (n = 8 per group). (D) Mass of the liver, WAT, BAT, and cecum (n = 8 per group). (E) Hepatic TG contents (n = 8 per group). (F) Blood glucose level (n = 8 per group). (G) Plasma insulin level (n = 7 per group). (H) Plasma levels of total cholesterol, NEFAs, and TG (n = 8 per group). All data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 (Mann–Whitney U test). HFD, high-fat diet; WAT, white adipose tissue; Epi, epididymal white adipose tissue; peri, perirenal white adipose tissue; sub, subcutaneous white adipose tissue; BAT, brown adipose tissue; TG, triglyceride; NEFAs, non-esterified fatty acids.