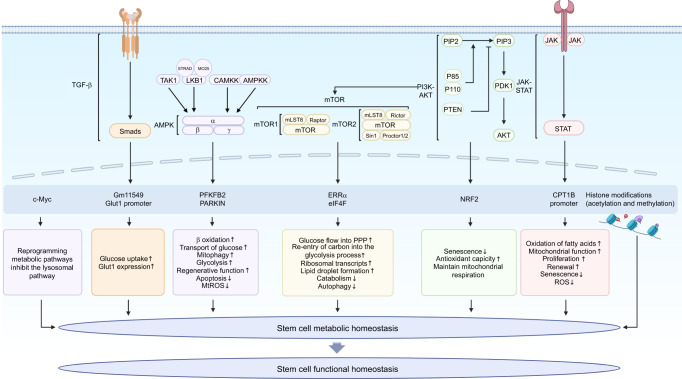
Fig. 5.
Molecular mechanisms of metabolic homeostatic regulation in stem cells. Stem cells regulate metabolic levels through a three-dimensional cellular metabolic-regulatory network that regulates downstream target genes and transcription factors to carry out a variety of metabolic processes, including glucose uptake, β-oxidation, autophagy, and so on, so as to maintain a dynamic balance under normal physiological conditions. Created with BioRender. TGF-β transforming growth factor-β, AMPK adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, LKB1 liver kinase B1, STRAD sterile 20 related adaptor protein, MO25 mouse protein 25, CAMKK2 calcium-sensitive kinase 2, TAK1 transforming growth factor β-activated kinase-1, AMPKK AMP-activated protein kinase kinase, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, mTORC1 mTOR complex 1, mTORC2 mTOR complex 2, mLST8 mTOR-associated protein LST8 Homolog, Sin1 stress-activated protein kinase-interacting protein, PI3K-AKT phosphoinositide-3-kinase AKT, PIP2 phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, PIP3 phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate, PTEN phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten, PDK1 phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1, STAT signal transducer and activator of transcription, PFKFB2 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 2, ERRα estrogen-related receptor α, eIF4F eukaryotic initiation factor 4F, NRF2 nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, PPP pentose phosphate pathway, mtROS mitochondrial ROS