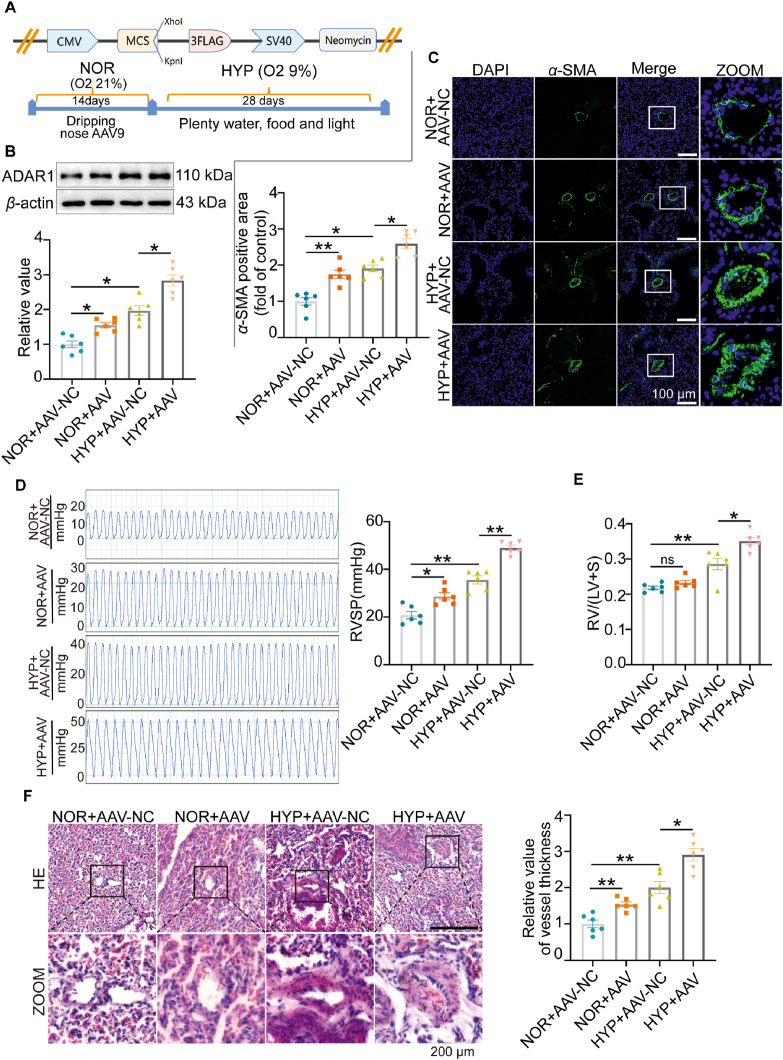
Figure 2.
Overexpression of ADAR1 aggravated hypoxia-induced PH in vivo. (A) Schematic illustration showing the construction of mice adeno-associated virus vector 9 (AAV9) plasmid and the treatment protocol. Mice were infected with AAV9 once a day for 14 days in normoxia situation and exposed to hypoxia for 28 days. (B) Representative Western blots and group data showing the expression of ADAR1 upon AAV9 treatment, n = 6. (C) Immunofluorescence assay showing the muscularization of vessels in mice infected with OE-ADAR1-AAV9, n = 6. (D, E) Hemodynamic assay showing that OE-ADAR1 aggravated Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP), and right ventricle (RV)/left ventricle (LV)+S weight ratio, n = 6. (F) Hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE) staining assay showing that OE-ADAR1 exacerbated pulmonary artery vascular remodeling, n = 6. NOR, normoxia; HYP, hypoxia, NC, negative control; ns, no significance; Statistical analysis was performed with two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test; All values are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.