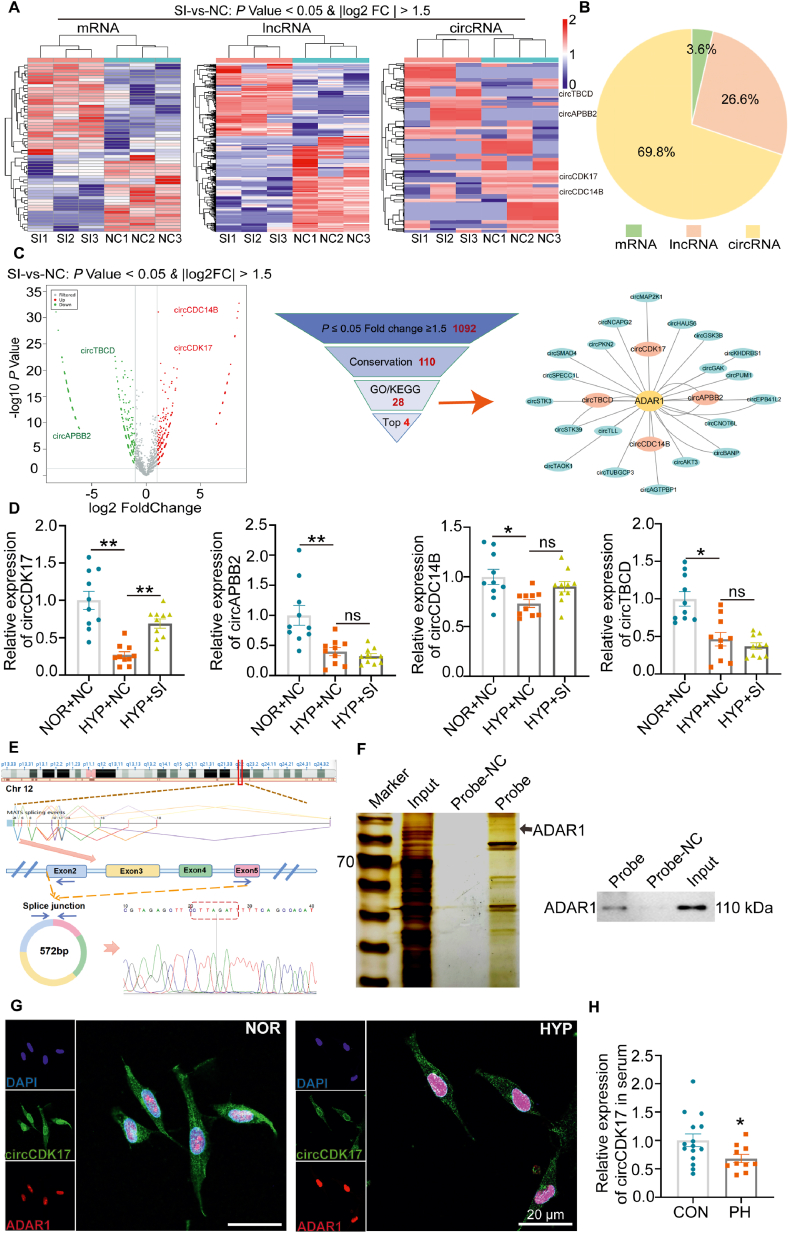
Figure 5.
ADAR1 regulated circular RNA-circCDK17. (A–B) High-throughput whole transcriptome sequencing showing the RNA changes upon silencing of ADAR1 (A) and the proportion of different types of RNA regulated by ADAR1 (B). (C) Volcanic map of differentially expressed circRNA after silencing of ADAR1, and screening of candidate circRNAs regulated by ADAR1. (D) qPCR analysis showing the expression of circCDK17, circAPBB2, circCDC14B and circTBCB upon silencing of ADAR1, n = 6. (E) Specific primers were designed for circCDK17 cycle-site for qPCR verification, and Sanger sequencing was performed to verify the accuracy of cycle-site. (F) RNA pull-down experiment showing that circCDK17 bound directly to ADAR1, n = 3. (G) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) showing the colocalization of ADAR1 and circCDK17. (H) qPCR analysis showing the expression of circCDK17 in serum of PH patients (CON = 15, PH = 10). CON, Control; PH, Pulmonary hypertension; NOR, normoxia; HYP, hypoxia; NC, negative control; SI, siRNA of ADAR1; Statistical analysis was performed with two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test or the Student's t-test; All values are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.