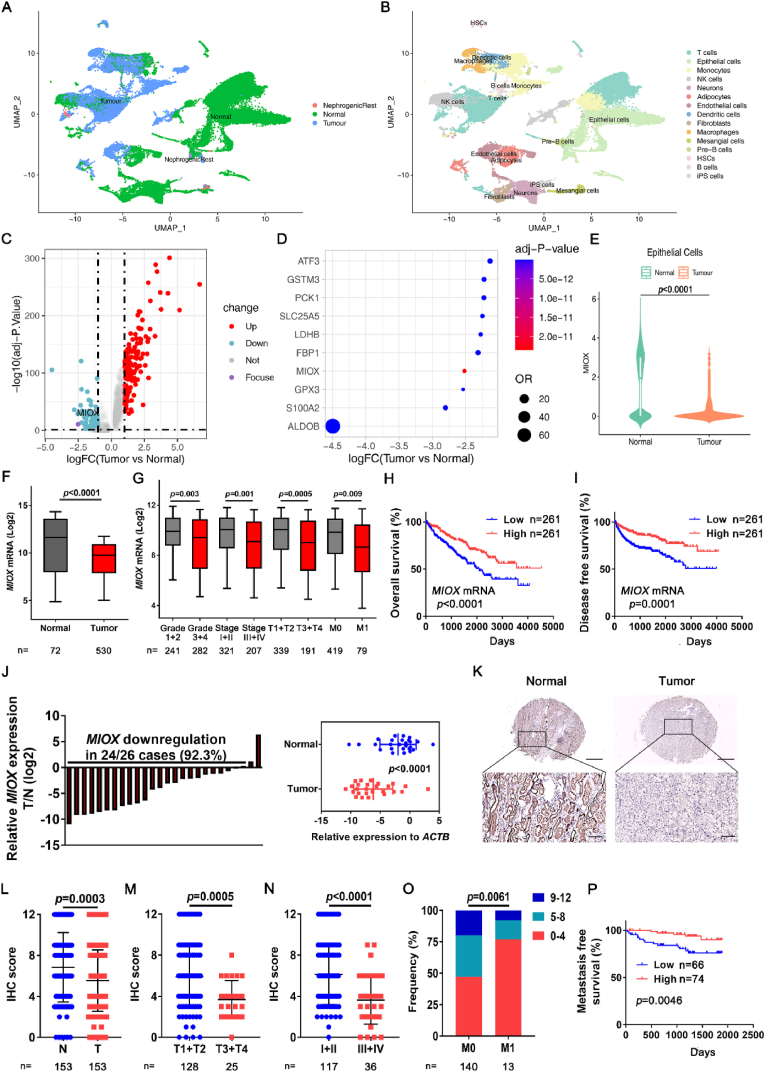
Fig. 1.
Identification of MIOX as a suppressor gene of ccRCC. (A-B) Single cell of 12 tumor samples and 9 adjacent normal samples of ccRCC in scRNA-seq database was classified according to normal and tumor tissues (A) and cell types (B). (C) Volcano plot of DEGs between tumor epithelial cells and normal epithelial cells. Up-regulated (log2 FC > 1.0) genes are marked in red and down-regulated genes (log2 FC < −1.0) are marked in blue. (D) The top 10 down-regulated genes in tumor epithelial cells compared to normal epithelial cells. (E) The expression of MIOX in normal epithelial cells and tumor epithelial cells in scRNA-seq database. (F) The expression of MIOX in adjacent normal tissues (Normal) and tumor tissues (Tumor) in TCGA ccRCC database. (G) The expression of MIOX in subgroups of patients with different Furhman grades (Grade 1–4), clinical stage (Stage I-IV), tumor stage (T1-T4), and metastatic status (M0 or M1) in the TCGA database. (H–I) Association of MIOX expression with OS (H) and DFS (I) of ccRCC patients in the TCGA database. (J) Detection of mRNA expression levels of MIOX in 26 pairs of ccRCC tissues (T) and adjacent normal tissues (N) by qRT-PCR (left panel), and the statistical analysis of relative expression levels of the reference gene ACTB showed in the right panel. (K-L) Representative images (K) and IHC score (L) of MIOX IHC staining of paired adjacent and ccRCC tissues in TMA. Scale bar: 500 μm for images above and 100 μm for images below. (M-N) MIOX staining scores in T1-T4 tumor (M) and clinical stage I-IV (N). (O) Frequency of different MIOX staining score groups in patients of stage M0 and M1. (P) Association of MIOX expression with MFS of ccRCC patients undergoing surgery at our center. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)