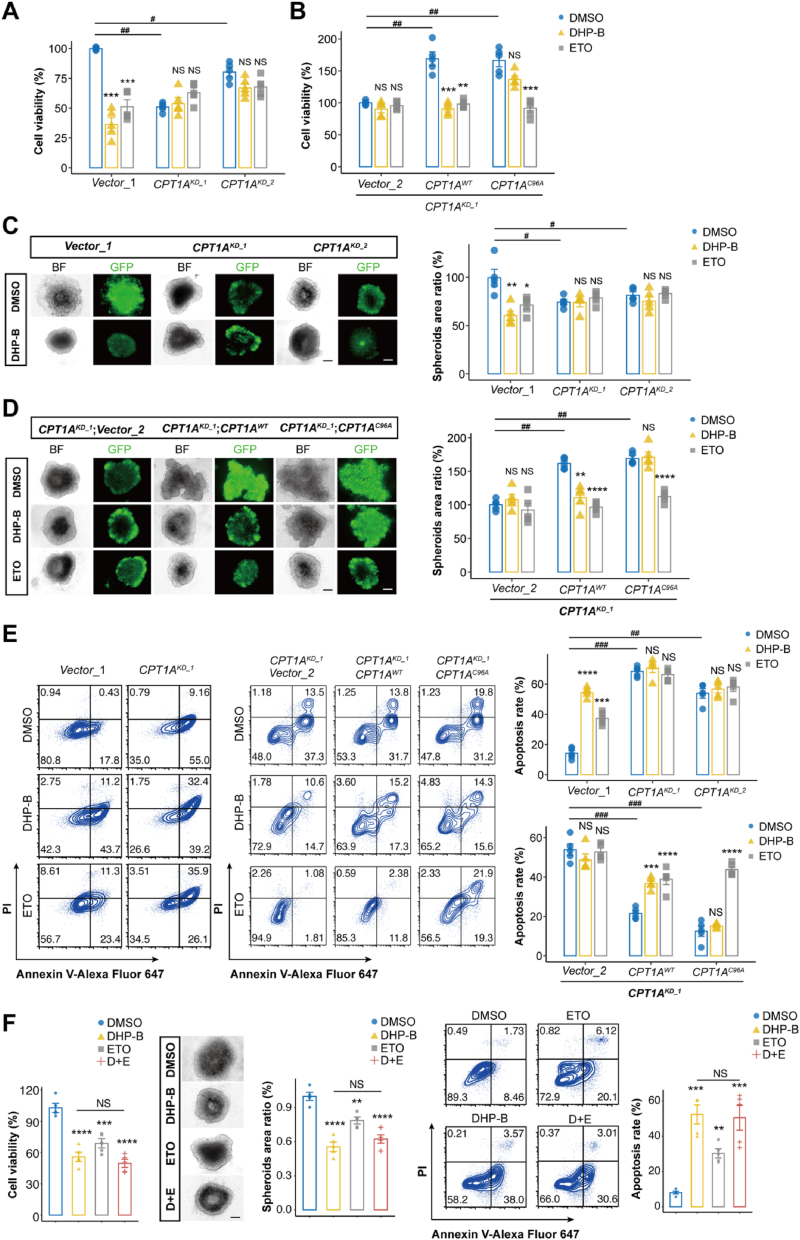
Fig. 5.
CPT1A is the anti-colorectal cancer target of DHP-B at the cellular level. (A) Cell proliferation of SW620 cells with CPT1A knockdown (CPT1AKD−1, CPT1AKD−2) or control (Vector_1) treated with DMSO, DHP-B (5 μM), or ETO (100 μM); (B) Cell proliferation of SW620 CPT1AKD−1 cells stably expressing vector (Vector_2), wild-type CPT1A (CPT1AWT), or C96A mutant CPT1A (CPT1AC96A) treated with different drugs. (C) 3D spheroid growth of SW620 cells with CPT1A knockdown or control treated with different drugs. Representative images and quantification of spheroid area are shown (scale bar: 100 μm); (D) 3D spheroid growth of CPT1AKD−1 SW620 cells stably expressing Vector_2, CPT1AWT, or CPT1AC96A treated with different drugs. Representative images and quantification of spheroid area are shown (scale bar: 100 μm); (E) Cell apoptosis of SW620 cells with CPT1A knockdown or control (left panel) or SW620 CPT1AKD−1 cells stably expressing CPT1AWT, or CPT1AC96A (right panel) treated with different drugs. Representative flow cytometry plots and quantification of apoptotic cells are shown; (F) Cell proliferation (left), 3D spheroid growth (middle), and cell apoptosis (right) of SW620 cells treated with DMSO, DHP-B, ETO, or their combination, respectively. Representative images, flow cytometry plots, and quantification are shown. Scale bar, 100 μm. All of the studies above were examined using at least five biological replicates, and the results were expressed as mean ± SD; NS, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, upaired t-test.