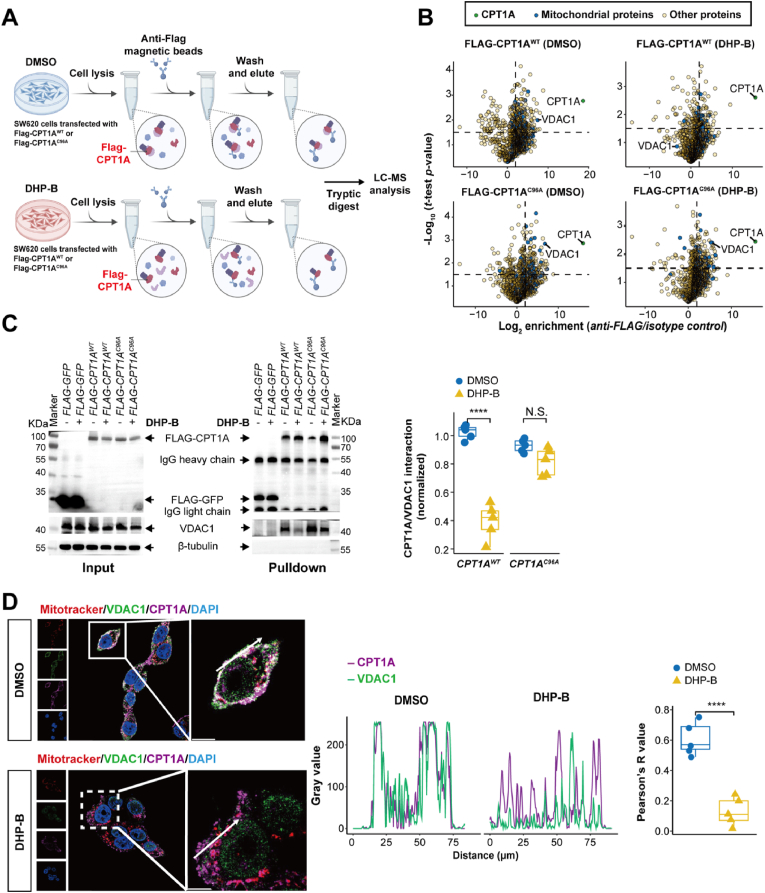
Fig. 8.
Identification and validation of VDAC1 as a key binding partner of CPT1A that regulates CRC cell apoptosis. (A) Schematic diagram of the MS-based CO-IP pulldown screening protocol; (B) Volcano plots showing the differential protein enrichment between anti-FLAG Co-IP and isotype control Co-IP (n = 3). The cutoff criteria for enrichment factor were log2 = 2 (4-fold enrichment) and -log10 (t-test P-value) = 1.5. FLAG-CPT1AWT or FLAG-CPT1AC96A are highlighted in green, and mitochondrial proteins are marked in blue; (C) Western blot analysis of the interacting proteins of FLAG-GFP(GFP), FLAG-CPT1AWT, or FLAG-CPT1AC96A in SW620 cells treated with DMSO or DHP-B (5 μM) for 24 h. Representative blots are shown, indicating the specific interaction of VDAC1 with CPT1A, which was significantly reduced by DHP-B treatment. The CPT1AC96A mutant protein also interacted specifically with VDAC1, but this interaction was not affected by DHP-B treatment; (D) Fluorescence microscopy images of the co-localization of CPT1A (purple) and VDAC1 (green) on mitochondria (red) in SW620 cells before and after DHP-B treatment (5 μM) (left panel). The white arrow points to the statistical cross-sectional area of co-localization of CPT1A and VADC1 proteins. The Pearson's R value of the fluorescence signals of CPT1A and VDAC1 before and after DHP-B treatment was calculated and quantified using the Coloc 2 plugin in Image J to determine the level of co-localization between them (right panel). All above experiments were performed with at least five biological replicates, and the results were expressed as Median ± IQR or otherwise stated; NS, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, unpaired t-test. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)