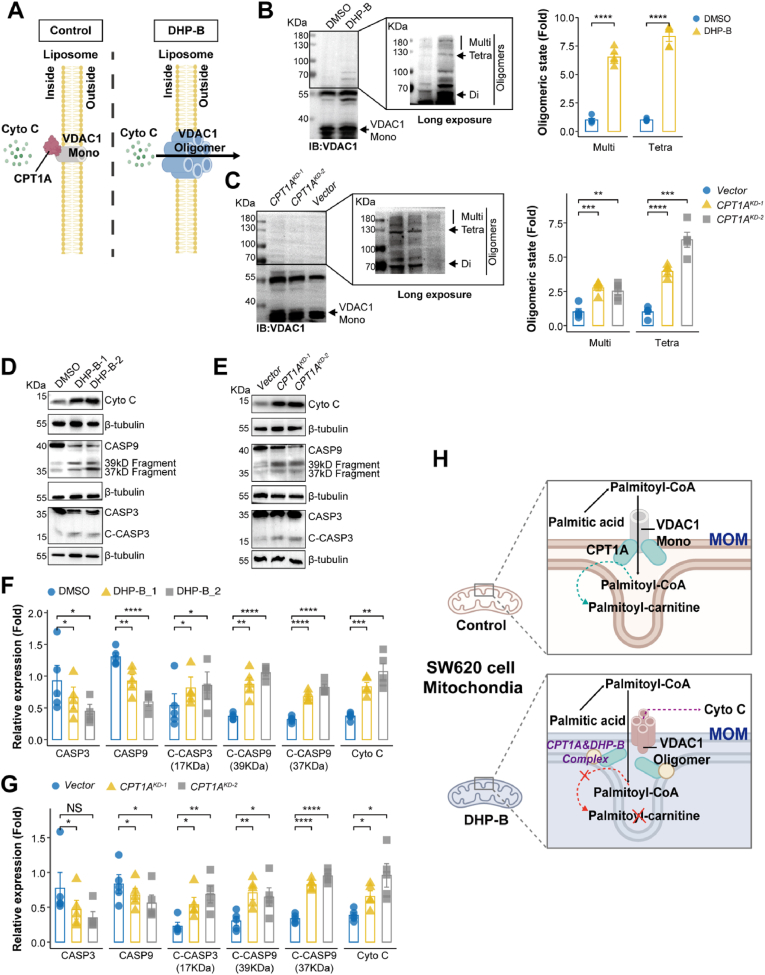
Fig. 9.
DHP-B targets the CPT1A-VDAC1 axis, induces VDAC1 oligomerization, and triggers CRC cell apoptosis. (A) Schematic diagram of the mechanism by which DHP-B inhibits the binding of CPT1A and VDAC1, induces VDAC1 oligomerization, increases mitochondrial membrane permeability, promotes the release of cytochrome C from mitochondria, and leads to tumor cell apoptosis; (B) Immunoblot analysis of the oligomerization of purified VDAC1 after treatment with DHP-B and the cross-linking reagent EGS to stabilize the oligomers during electrophoresis (left panel). The positions of VDAC1 monomers (Mono), dimers (Di), tetramers (Tetra) and multimers (Multi) are indicated. Quantification of oligomers is shown in the right panel; (C) Immunoblot analysis of the oligomerization of VDAC1 in SW620 cells with or without CPT1A knockdown (Vector and CPT1AKD−1, respectively) after treatment with DHP-B. The positions of VDAC1 monomers (Mono), dimers (Di), tetramers (Tetra) and multimers (Multi) are indicated (left panel). Quantification of oligomers is shown in the right panel; (D&F) Western blot analysis of the expression levels of cytochrome C (Cyto C), CASP9, cleaved CASP9 (C-CASP9, 39&37 kDa), CASP3 and cleaved CASP3 (C-CASP3, 17 kDa) proteins in SW620 cells after treatment with DHP-B (5 μM); (E&G) Western blot analysis of the expression levels of Cyto C, CASP9, C-CASP9, CASP3 and C-CASP3 proteins in SW620 cells after CPT1A knockdown; (H) Schematic diagram summarizing the mechanism by which DHP-B inhibits CRC cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting CPT1A. All experiments were performed with at least five biological replicates, and the results were expressed as mean ± SD or otherwise stated; NS, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, unpaired t-test.