FIGURE 5.
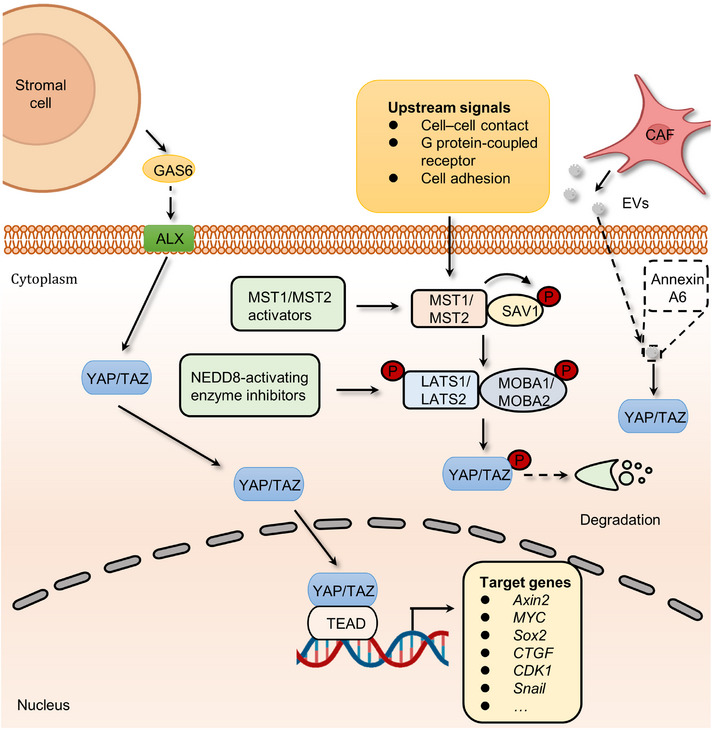
The mechanism by which cancer cells utilize the Hippo signaling pathway and associated therapeutic targets. The core proteins of Hippo pathway include MST1/2, LATS1/2, SAV1, MOB1A/1B, and YAP1/TAZ. Once activated by upstream signals, MST1/2 can phosphorylates SAV1, which subsequently activates LATS complex comprising LATS1/2 and MOB1A/1B. Then, the activated LATS complex phosphorylates YAP1/TAZ, thereby leading to the degradation of transcriptional factors of Hippo pathway. Otherwise, YAP1/TAZ can translocate to the nucleus and bind with TEA domain (TEAD) family members to promote the expression of Hippo signaling target genes. Stromal cells‐secreted GAS6, and CAF‐derived EVs (encompassing Annexin A6) mediate YAP/TAZ shuttling to the nucleus, which favors the expression of drug resistance‐related genes. MST1/2 activators and NEDD8 activating enzyme inhibitors were developed to prevent the transcription of Hippo pathway target genes, thereby increasing the degradation of YAP1/TAZ.
