FIGURE 6.
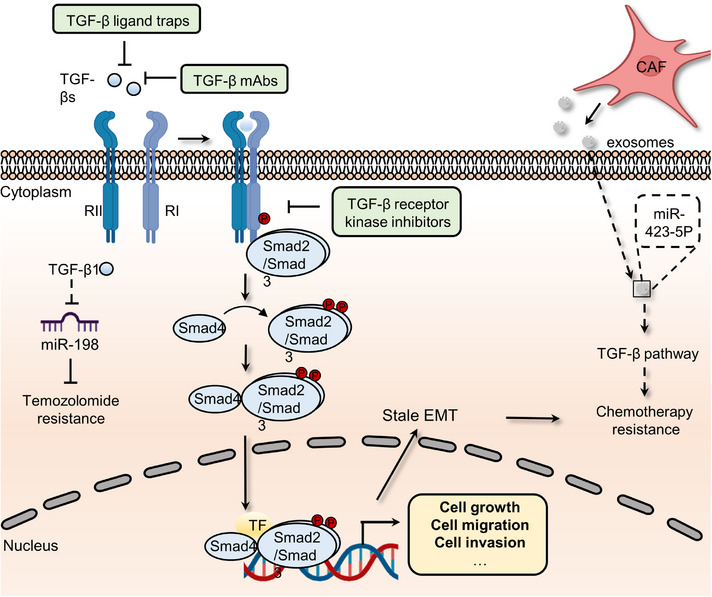
The roles of canonical TGF‐β signaling pathway in cancer and inhibitors that target TGF‐β pathway. The ligands, TGF‐βs, bind TGF‐β type II (RII) induce the phosphorylation of TGF‐β type I (RI) receptors on cell surface. Activated kinase activity of RI further phosphorylates Smad2 and Smad3, which form trimeric complexes with Smad4. These Smad complexes will translocate into nucleus and promote the transcription of TGF‐β pathway downstream genes. Sustained activation of TGF‐β signaling can lead to cancer drug resistance via inducing stable epithelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition (EMT) and regulating the expression of miR‐198 or miR423‐5p. Hence, agents, such as TGF‐β ligand traps, TGF‐β mAbs, and TGF‐β kinase inhibitors, have been developed to impair the activation of TGF‐β signaling pathway.
