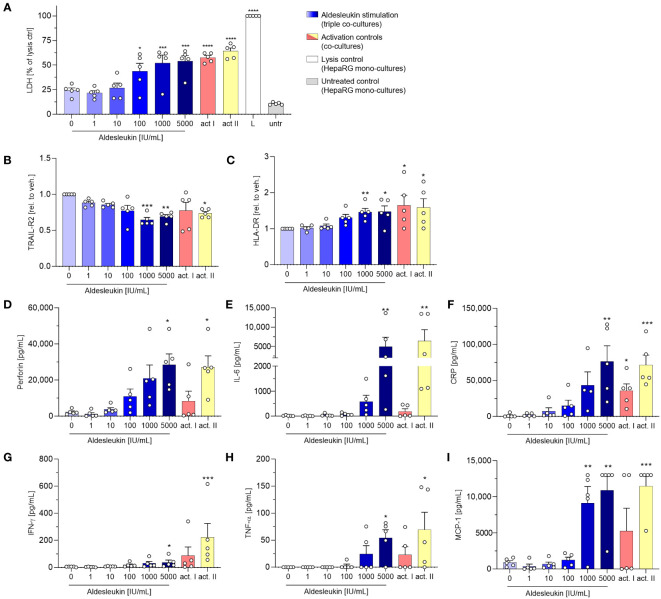
Figure 6.
Addition of monocyte-derived macrophages to CD8+ T cell/HepaRG co-cultures enhances aldesleukin-induced pro-inflammatory effects. Primary human CD8+ T cell/monocyte-derived macrophage (MdM) co-cultures were treated with aldesleukin or activation controls (act I, CD3/CD28 + rhIL-2 activation; act II, PHA-L+ rhIL-2 activation) and co-cultured with HepaRG cells in direct co-cultures. (A) For cytotoxicity assessment, CD8+ T cell/MdM mixtures were co-cultured with HepaRG cells for 5 d. Colorimetric assessment of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity was conducted to measure cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Samples were referred to the lysis control. (B-I) 3 days pre-stimulated CD8+ T cell/MdM co-cultures were co-cultured with HepaRG cells for additional 2 days. (B, C) Hepatic surface marker expression was measured with flow cytometry and the mean fluorescence intensity was related to the vehicle control. (D-I) Pro-inflammatory mediators were quantified via flow cytometry; CRP was determined via ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. N = 5 biological replicates were evaluated. Per biological replicate, one technical replicate was acquired. For statistical analysis of (I) one-way ANOVA with Dunnett´s multiple comparison test was used and for analysis of (A-I) Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn´s correction was applied. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001 indicate significant differences between aldesleukin-treated or activated and vehicle-treated samples. CRP, c-reactive protein; IFN-γ, Interferon-γ; IL-6, Interleukin-6; L, Triton-X-lysed HepaRG control; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; untr., untreated HepaRG monocultures.