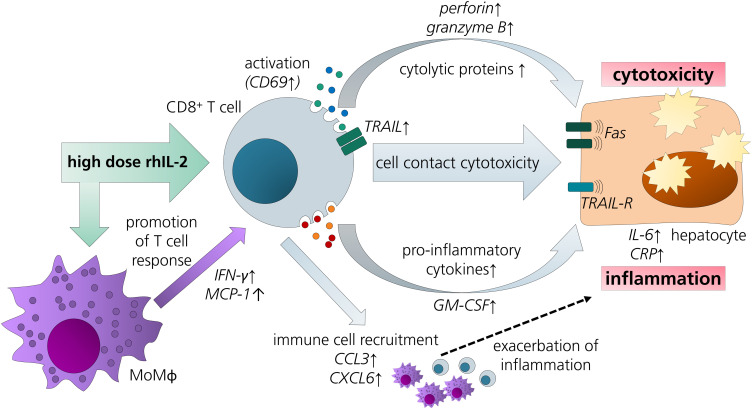
Figure 8.
Overview of potential pathways and key players in aldesleukin-mediated hepatotoxicity. Upon high-dose aldesleukin (rhIL-2), CD8+ T cells were activated and in direct co-cultures with the HepaRG cell line and primary human hepatocytes, cytotoxic molecules such as perforin and pro-inflammatory mediators such as c-reactive protein were induced. Direct cell-cell contact was necessary to induce a cytotoxic effect. Proteomic analyses point towards the recruitment of further immune cells, such as T cells and monocytes. Addition of monocyte-derived macrophages to the co-cultures enhanced the pro-inflammatory response. CCL3, Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3; CXCL6, Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6; CRP, C-reactive protein; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL-6, interleukin 6; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; MoMΦ, monocyte-derived macrophage; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; TRAIL-R, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor.