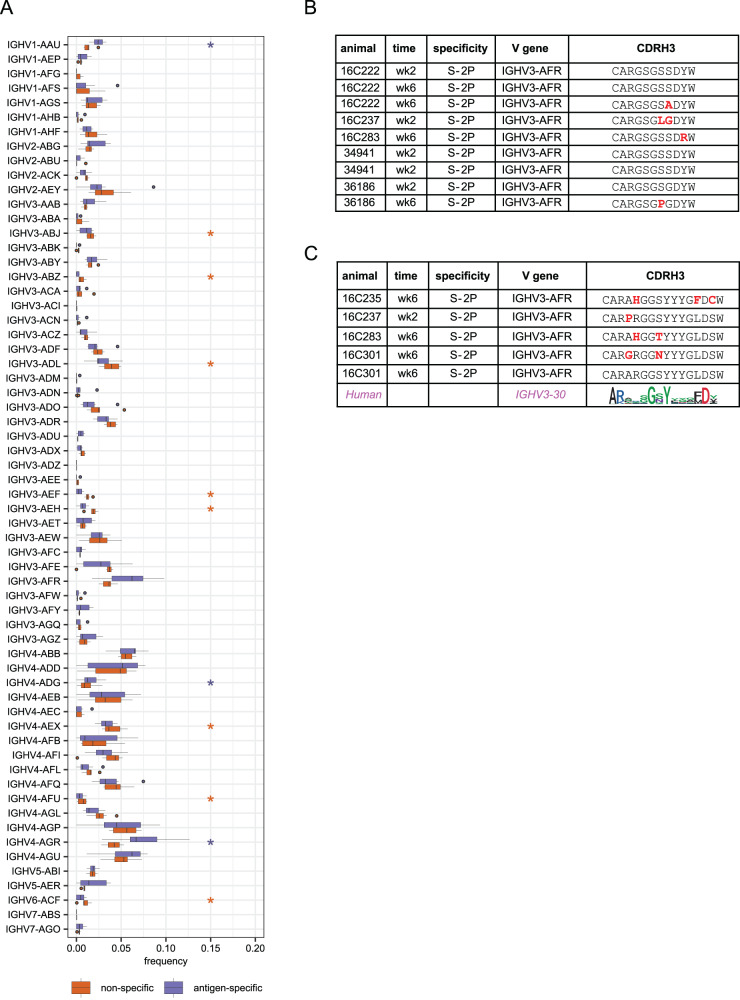
Fig. 3. V gene usage and public clones.
A Comparison of VH gene usage between all naïve B cells (orange) and antigen-specific memory B cells (purple) from seven animals (animal 16C237 was excluded due to lack of naive repertoire data). Boxes show the interquartile range, with the median marked as heavy horizontal band. Whiskers represent the highest (lowest) datapoint within 1.5 times the interquartile range of the 75th (25th) percentile. N = 1706 antigen-specific lineages and 29,161 sorted naive B cells. Genes with statistically significant differences by a 2-sided paired Wilcoxon test are indicated with asterisks in the color of the up-regulated group. P = 0.016 for IGHV1-AAU, IGHV3-AEF, IGHV4-AFU, IGHV4-AGR, and IGHV5-AER. P = 0.031 for IGHV3-ABZ, IGHV3-AEH, and IGHV4-ADG. P = 0.047 for IGHV3-ABJ, IGHV3-ADL, and IGHV4-AEX. B A public B cell clone using IGHV3-AFR that was found in five of eight vaccinated animals. Residues that differ from the consensus are highlighted in red. Two identical rows indicate two cells with the same amino acid CDR H3 found in a single animal and time point. C A second public clone was found in four animals. The consensus of a corresponding human public clone is shown as a logo plot. Conserved positions in the human public clone, which are hypothesized to be functionally important, are also conserved in the rhesus public clone. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.