Figure 3. Increased light scattering of deamidated human γS crystallin.
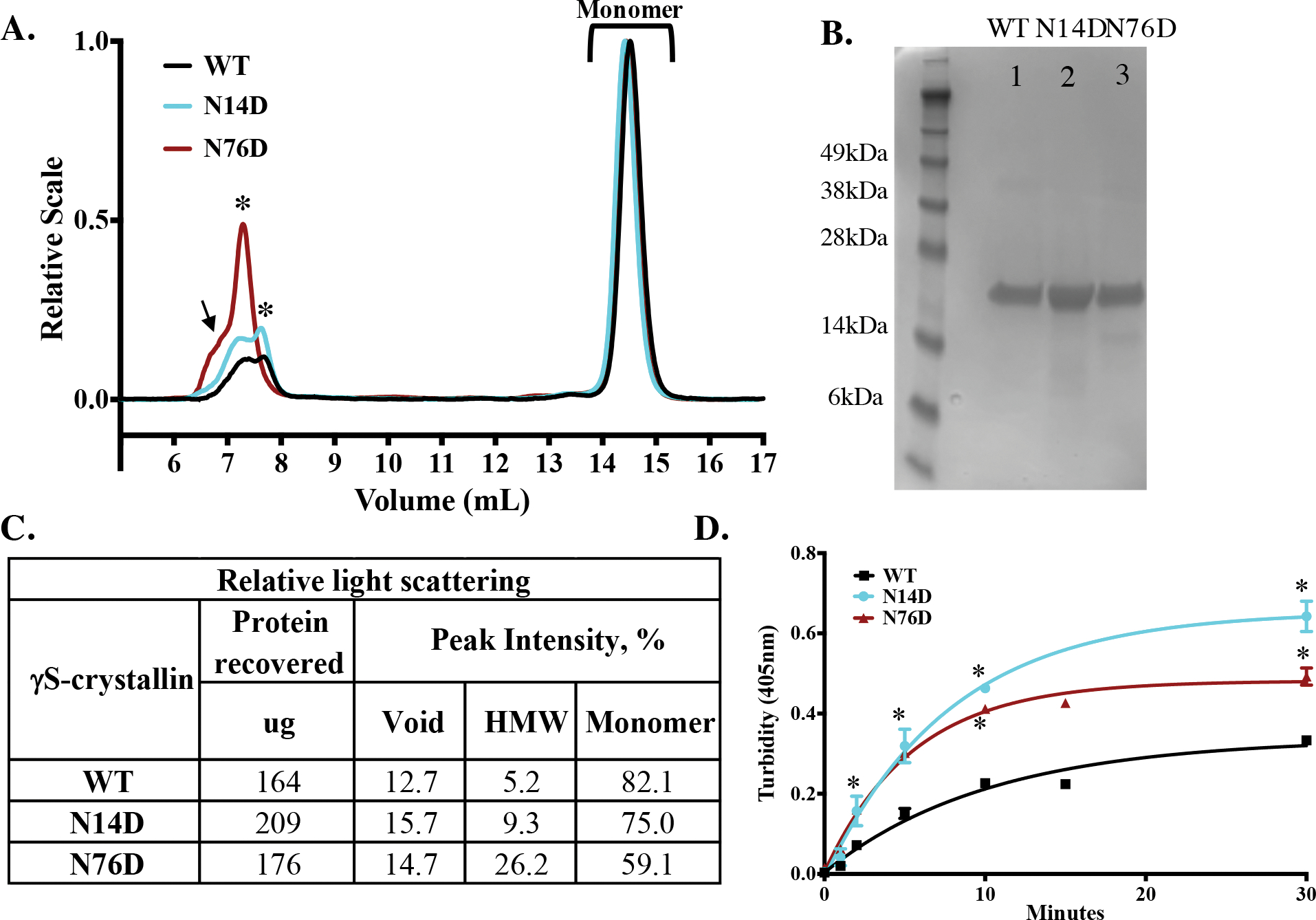
(A) Relative Rayleigh light scattering traces of γS WT (black), N14D, (cyan) and N76D (dark red) during size-exclusion chromatography in-line with multiangle laser scattering. A high molecular weight peak (HMW, starred) was detected just after the void peak (arrow). (B) SDS-PAGE of WT (Lane 1), N14D (Lane 2) and N76D (Lane 3) γS-crystallins. (C) Table of relative light scattering intensity of peaks from B. (D) Relative turbidity of γS-crystallins during thermal-induced denaturation at 70 °C of WT (black), γS N14D (cyan), and γS N76D (red). Turbidity measured as change in O.D. at 405 nm, n=3 and SEM calculated via 2-way ANOVA with p < 0.05 (*). Curve fits were generated using nonlinear regression with PRISM 6. Initial rates of increase in turbidity were 0.03 min−1 for WT and 0.06 min−1 for N14D and N76D.
