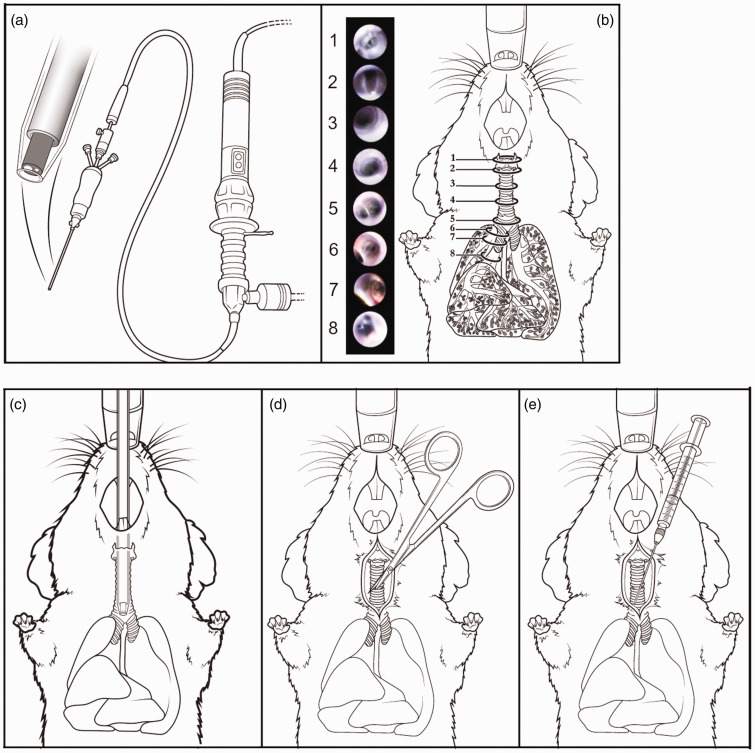
Figure 1.
The endoscopic system for accessing the airways compared with the transtracheal procedure. (a) The bronchoscope contains a fiber optic to guide the user through the airway. Images obtained from the fiber optic are shown in pictures 1–8, and the sites corresponding to the images are shown in (b). The tip is introduced through the mouth and proceeds into the trachea. The vocal cords and larynx are observed first (1), and upon opening of the vocal cords (2), the catheter proceeds into the trachea (3 and 4) to the carina (5) and into the right main stem bronchus (6 and 7) where the next generation of bronchioles are visualized (8) but are too small for the catheter to enter. (c) The endoscope sheathed with a removable catheter is inserted through the mouth of the mouse and enters the trachea through the epiglottis and the vocal cords. (d) and (e) The transtracheal involves a 0.5-cm incision in the skin to expose the trachea and a subsequent small incision between the cartilage rings through which a gavage needle is inserted to administer substances.