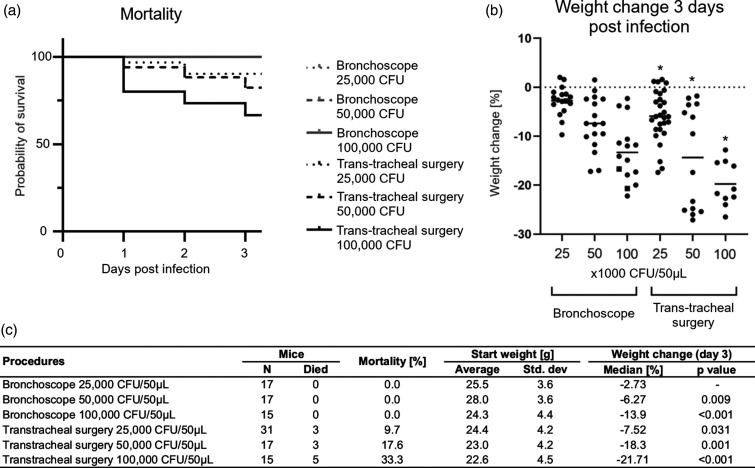
Figure 5.
Effect of procedure on survival and weight change. Three different inoculums of PAM bacteria embedded in agarose beads (25,000, 50,000, or 100,000 CFU) were instilled in the airways of mice via the bronchoscope or through transtracheal surgery. Mortality was observed in a dose-dependent manner only in animals that underwent transtracheal surgery (a). The percent weight change on day 3 (compared with the day of instillation of bacteria; day 0) also shows a dose-dependent weight loss using PAM bacteria (b). Mice that survived to day 3 are shown with a dot, and the lines represent the median for each group. *Some mice in the group died prior to day 3 and are not represented in the graph. Table C shows numbers of deaths after the different procedures and the calculated p-value of weight change on day 3 compared with 25,000 CFU PAM instilled using the bronchoscopic procedure. Weight change increases in a dose-dependent manner for both procedures, whereas numbers of mice that died only increased for the transtracheal procedure.