Figure 1.
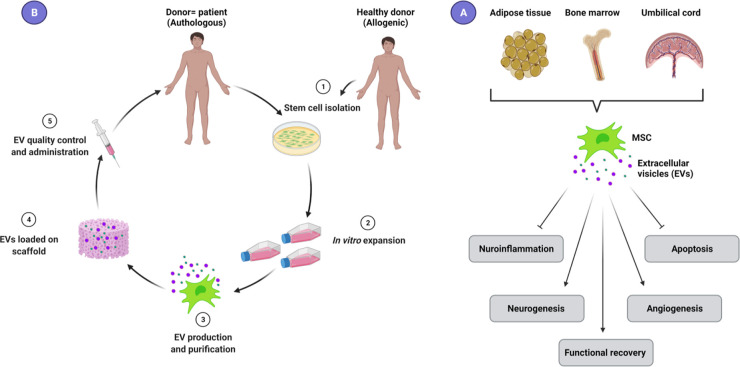
Most common sources of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord
A) Extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes and microvesicles are released from different cell types, including MSCs, and mediate the beneficial effects of MSCs on target cells. MSC-EVs reduce neuroinflammation by inhibiting the activation of astrocytes and microglia and switching to an anti-inflammatory phase. They also attenuate neuronal apoptosis, and promote angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and functional recovery in SCI patients.
B) EVs can be derived from the patient’s MSCs (authologous) or from healthy donors (allogenic) and then expand in vitro. In the next step, EVs are extracted and purified by various protocols based on different protein markers, sizes, and density of EVs. Isolated EVs following quality control can be administrated directly, or with biocompatible 3D scaffolds.