Fig. 4.
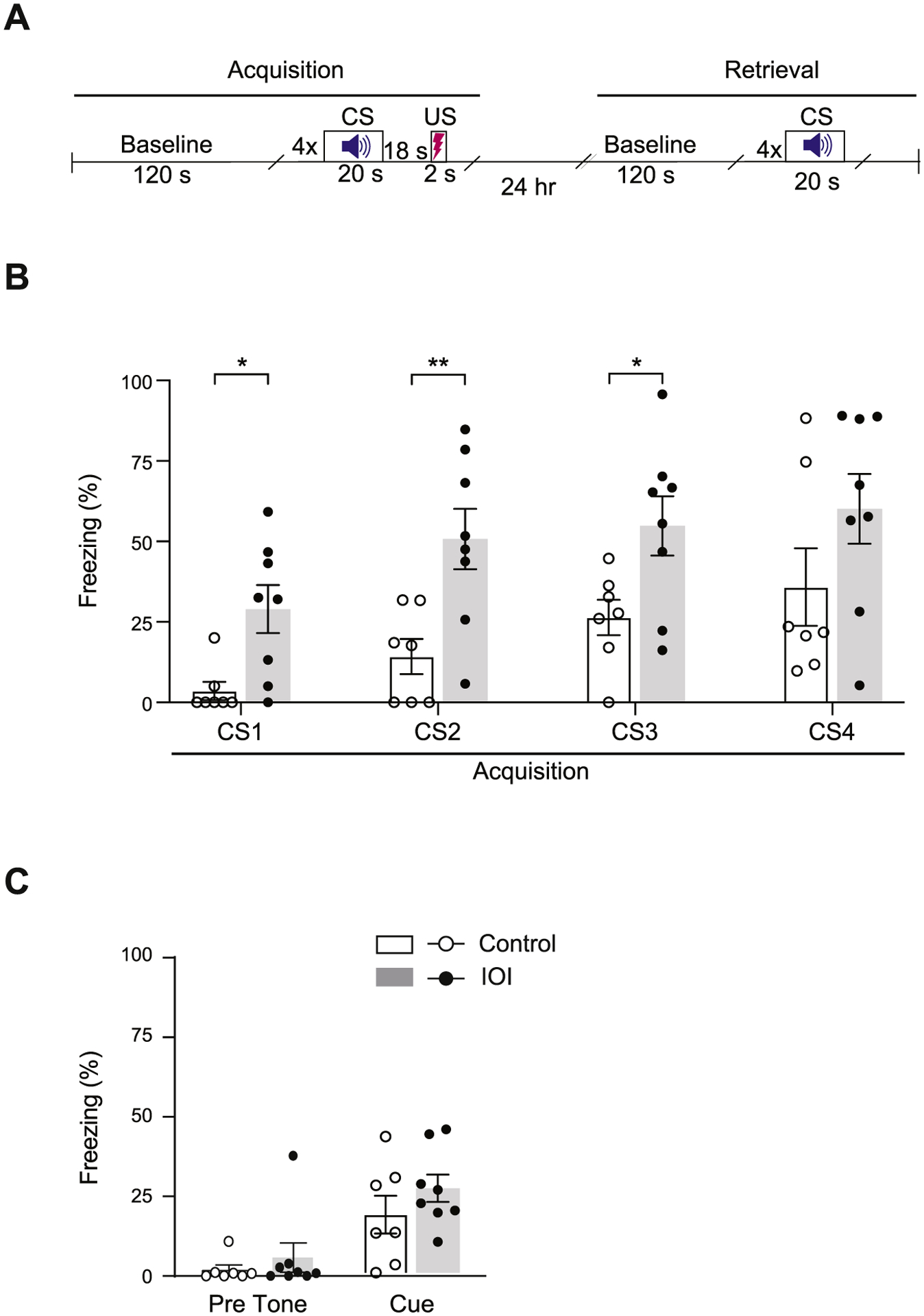
Chronic OE inflammation induces exaggerated fear responses to a discrete auditory cue. (A) Schematic diagram showing the experimental schedule of the trace fear conditioning test. CS: conditioned stimulus, US: unconditioned stimulus. (B) During the fear acquisition period, compared with controls, IOI mice showed a higher percent of time spent freezing as a response to a discrete auditory cue (CS) even before it was paired with a foot-shock (US), despite no significant effect of the CS on the group. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA for group x CS, F3,39 = 0.342, p = 0.795; Bonferroni’s post hoc tests with multiple comparisons were used to examine the differences between Control and IOI mice, CS1: p = 0.01, CS2: p = 0.0065, CS3: p = 0.0240, CS4: p = 0.1556. (C) In the cued fear retrieval phase, similar levels of freezing were displayed by IOI mice and controls before tone exposure (Pre tone), and there was no difference in freezing behavior between the two groups during auditory cue re-exposure in a different context. Two-way ANOVA for group x tone, F1,26 = 0.249, p = 0.622; Bonferroni’s post hoc tests with multiple comparisons were used to examine the differences between Control and IOI mice, Pre tone: p = 0.1968, Cue: p = 0.5412. bar graphs expressed as mean ± SEM; **p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05; IOI, n = 8 (7 male, 1 female); Control, n = 7 (6 male, 1 female).
