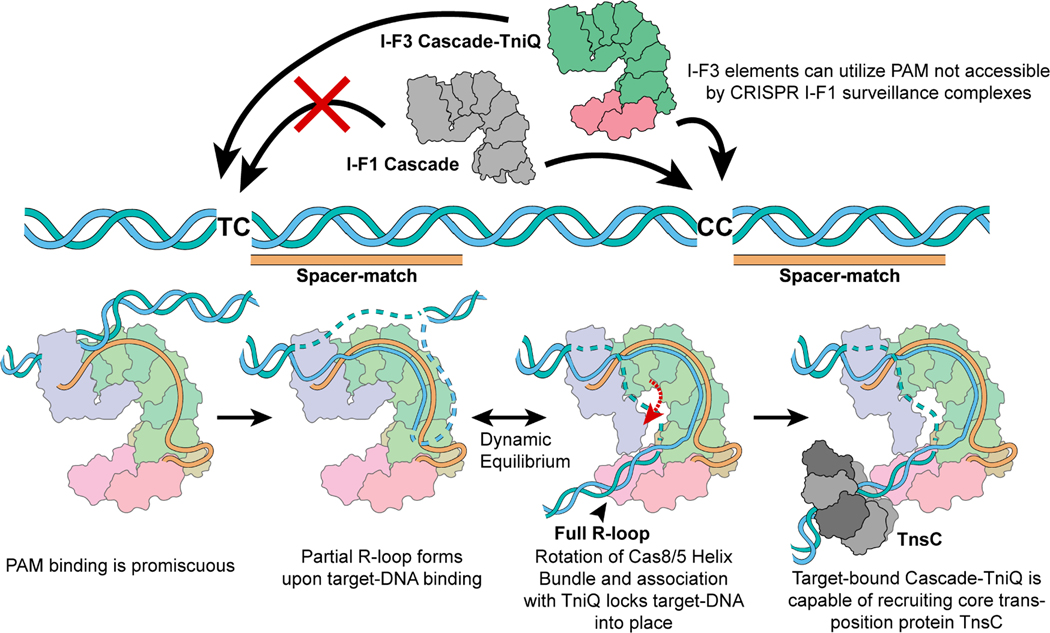
Figure 6. Schematic summarizing key mechanistic insights from this work.
I-F1 CRISPR surveillance complexes (grey) have stricter PAM sequence requirements. However, the I-F3 CAST family is able to make use of loosened PAM requirements. R-loop formation is accompanied by a conformational change in the Cascade complex and locks down on target-DNA via TniQ, revealing the mechanistic coupling between the CRISPR effector and core transposition protein, TniQ. This results in DNA distortions that most likely serve to recruit AAA+ regulator TnsC in order to direct DNA donor integration via the transposase, TnsA/B.