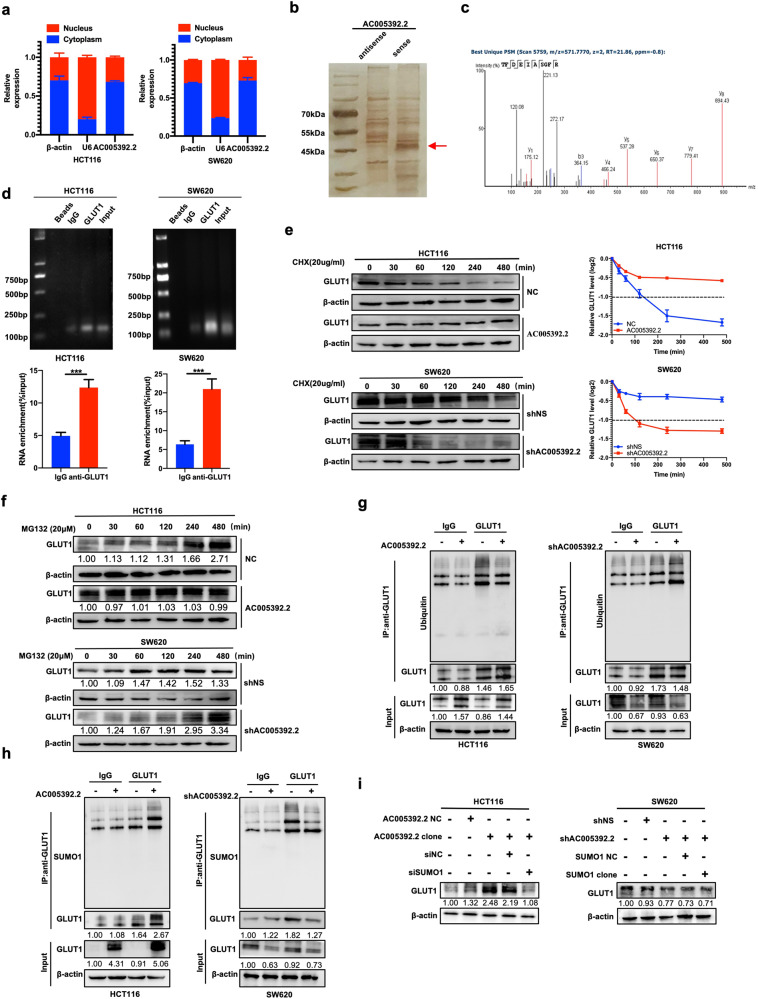
Fig. 4. AC005392.2 activates glycolysis by binding and increasing the stability of GLUT1 protein.
a qRT-PCR detection of AC005392.2 expression in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of HCT116 and SW620 cells (mean ± SD; n = 3). b Silver staining showing the stripes pulled down by the sense and antisense AC005392.2 sequences. The arrow indicates the candidate stripes. c Unique peptides of GLUT1 were detected by mass spectrometry. d RIP assay showing the enrichment of AC005392.2 in the complex coprecipitated by anti-GLUT1 antibody in HCT116 and SW620 cells (mean ± SD; n = 3, two-tailed Student’s t test). e, f HCT116 and SW620 cells were transfected for 72 h with an AC005392.2 clone or AC005392.2 shRNA, then treated with 20 μg/ml cycloheximide (e) or 20 μM MG132 (f) for the indicated time. Western blotting was performed to analyze the expression of GLUT1. g, h Immunoprecipitation followed by western blotting was performed to analyze the ubiquitination (g) and SUMOylation (h) of GLUT1 in AC005392.2-overexpressing HCT116 and AC005392.2-knockdown SW620 cells. i Western blotting analysis of the protein levels of GLUT1 in HCT116 cells co-transfected with AC005392.2 clone and SUMO1 siRNA or in SW620 cells co-transfected with AC005392.2 shRNA and SUMO1 clone for 72 h. ***p < 0.001.