Figure 1.
The activity-based assay predicts sensitivity to a PARPi
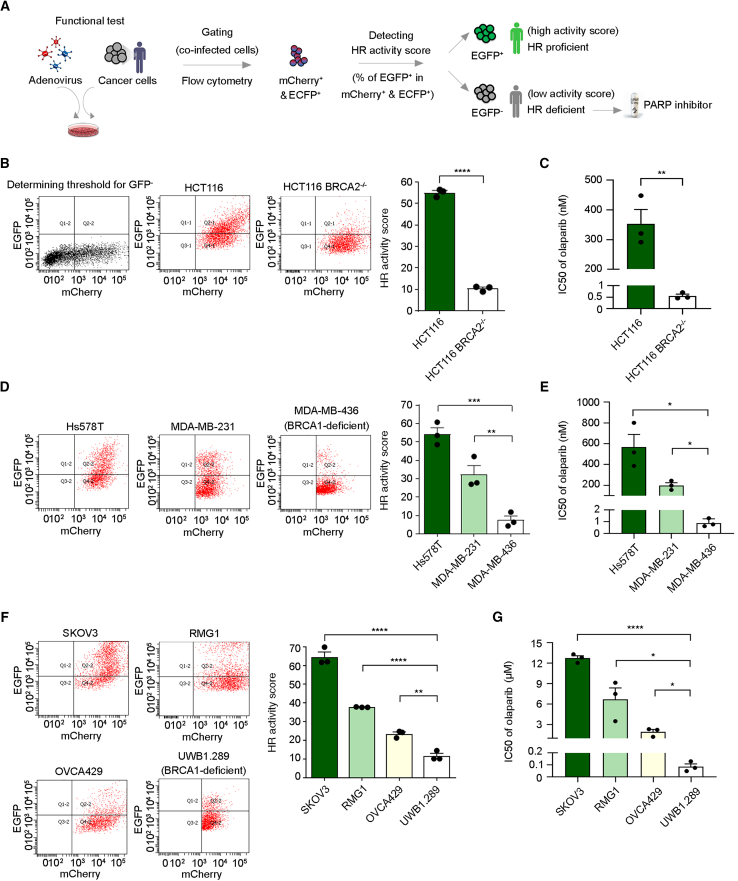
(A) Flowchart of the adenovirus-based detection method to assess cellular HR activity to accompany PARPi treatment as precision medicine.
(B) HR activity of parental or BRCA2-deficient colorectal carcinoma HCT116 cells was assessed 72 h after adenovirus infection.
(C) Viability of paired HCT116 cells was measured upon treatment with olaparib for 12 days to evaluate the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of olaparib.
(D) HR activity of triple-negative breast cancer cell lines Hs578T, MDA-MB-231, and BRCA1-deficient MDA-MB-436 cells was analyzed 72 h after adenovirus infection.
(E) Cell sensitivity to olaparib was measured after treatment with olaparib for 12 days.
(F) HR activity of ovarian cancer cell lines SKOV3, RMG1, OVCA429, and BRCA1-deficient UWB1.289 cells was assessed.
(G) Ovarian cancer cells were treated with olaparib for 12 days, followed by measurement of the IC50 of olaparib.
∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Data are the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (n = 3 biological replicates). Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test in (B) and (C) and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test in (D)–(G).
See also Figure S1.