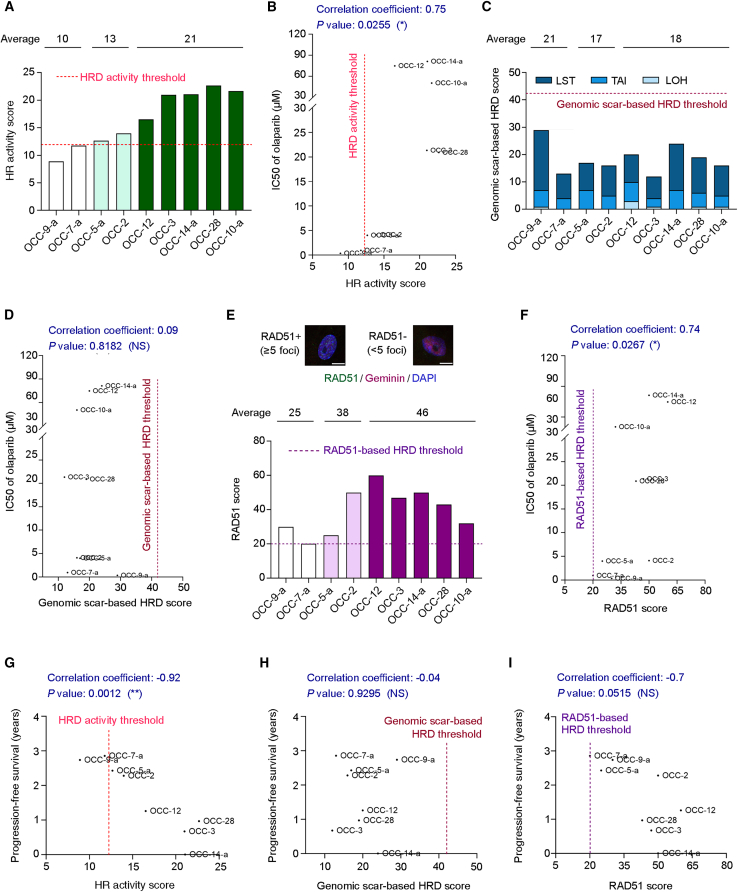
Figure 4.
HR activity scores correlate more strongly with PARPi sensitivity and clinical responses than the genomic-scar-based test and the RAD51 foci-based HRD assay
(A) The HR activity scores of nine primary ovarian cancer cell lines. The value of the HRD threshold for the activity-based functional test is 12.
(B) According to a Spearman correlation test, primary ovarian cancer cells can be classified as PARPi-susceptible cells (OCC-9-a and OCC-7-a; IC50 values: 0.35 and 0.94 μM, respectively), PARPi less sensitive cells (OCC-5-a and OCC-2; IC50 values: 4.01 and 4.11 μM, respectively), or PARPi-resistant cells (OCC-12, OCC-3, OCC-14-a, OCC-28, and OCC-10-a; IC50 values ranging from 20.9 to 81.3 μM). The correlation coefficient represents the strength of correlation between two variables.
(C) The genomic DNA of nine primary ovarian cancer cells mentioned in (A) was subjected to next-generation sequencing. Three indicators of HRD-associated genomic scar include large-scale transitions (LSTs), telomeric allelic imbalance (TAI), and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) events, which are summed and presented as genomic-scar-based HRD scores. The value of the HRD threshold for the genomic-scar-based analysis is 42.
(D) A Spearman correlation test was conducted to analyze the correlation between the genomic-scar-based HRD score and PARPi sensitivity of primary ovarian cancer cells.
(E) Primary ovarian cancer cells were co-stained for RAD51 and geminin, a marker of S/G2 cell phases, 2 h after 5 Gy radiation exposure. DNA was counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). The RAD51 scores, the percentage of geminin-positive cells with ≥5 RAD51 foci, of the nine primary ovarian cancer cells mentioned in (A) are shown. The value of the HRD threshold for the RAD51-based functional assay is 20. Scale bar, 10 μm. See also Figure S4.
(F) The relationship between the RAD51 scores and the PARPi sensitivity of primary ovarian cancer cells, as analyzed using the Spearman correlation test.
(G‒I) A Pearson correlation test was used to analyze the strength of the correlation between the duration of progression-free survival and (G) HR activity score, (H) genomic-scar-based HRD score, or (I) RAD51 score. A minus sign indicates an inverse relationship between two variables in the correlation test.
∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; NS, not significant (p > 0.05).