Figure 2.
Detection of the cancer genes using different types of variations
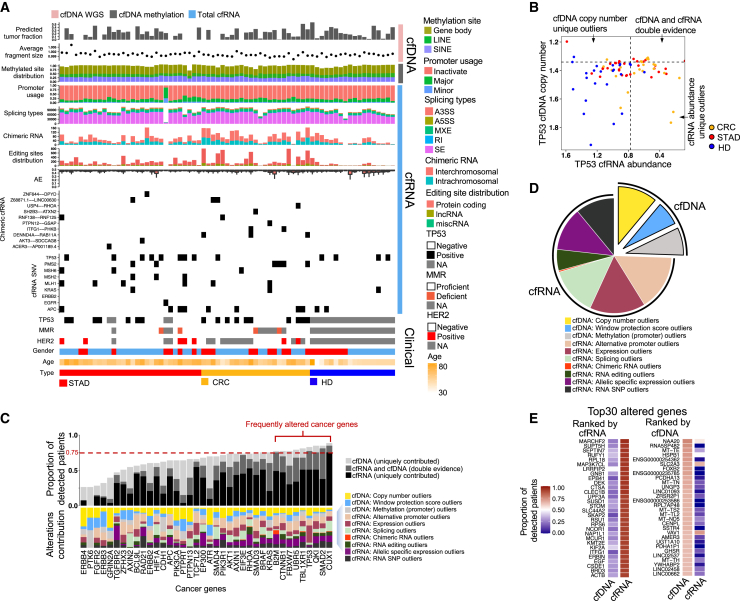
(A) Overview of the plasma multi-omics variation atlas (including 30 patients with STAD, 23 patients with CRC, and 18 HDs).
(B) cfDNA copy number and cfRNA abundance for TP53. HD, healthy donor; CRC, colorectal cancer; STAD, stomach adenocarcinoma. The dotted lines represent 95% specificity defined by HDs.
(C) Detection capacity for each cancer gene, combing different variations derived from cfDNA (cfWGS and cfMeDIP-seq) and total cfRNA-seq data. Frequently altered genes are defined by a greater than 75% detection ratio.
(D) Distribution of variation types among all genes that are frequently altered.
(E) Altered genes with top detection ratios ranked by cfRNA and cfDNA, respectively.