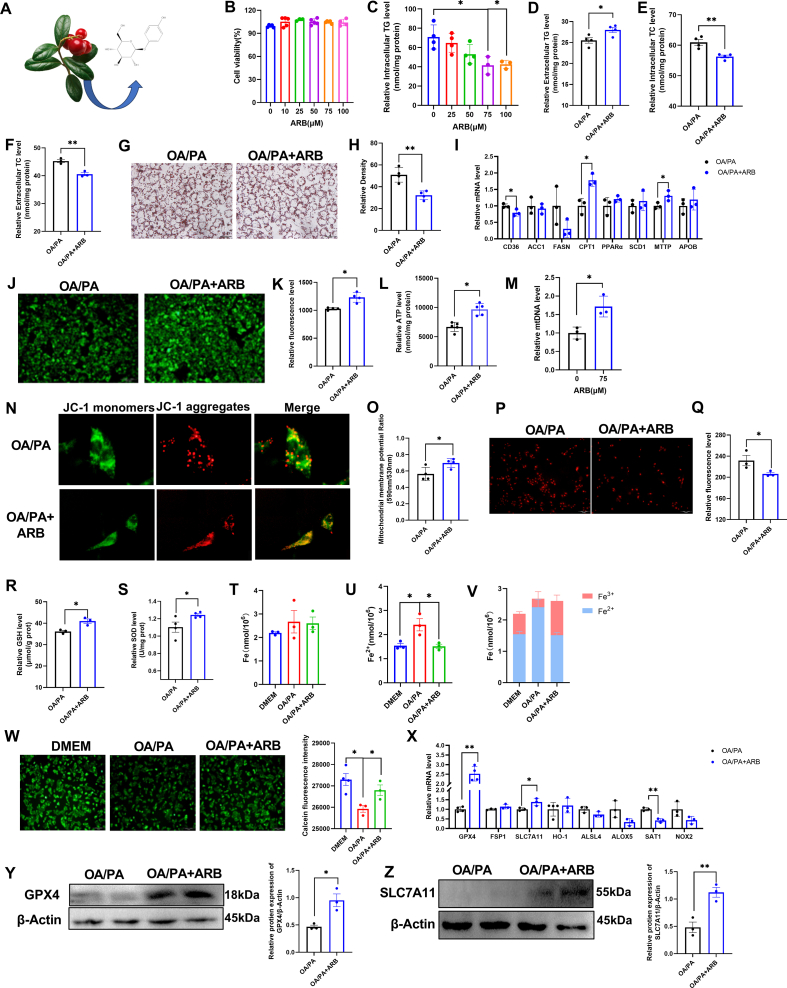
Fig. 1.
ARB regulates intracellular lipid deposition and ferroptosis. (A) Molecular structure of ARB. (B) CCK8 detects the effect of ARB on cell viability (n = 4–5 per group). (C–D) Intracellular and extracellular TG content under different concentrations of ARB treatment for 24 h (C: n = 3–4 per group, D: n = 4 per group). (E–F) Intracellular and extracellular TC content under different concentrations of ARB treatment for 24 h (E: n = 4 per group, F: n = 3 per group). (G–H) Oil red O staining and its quantification (n = 4 per group). (I) qPT-PCR of lipid metabolism-related genes (n = 3 per group). (J–K) Mitochondrial staining and its quantification (n = 4 per group). (L) Effect of 75 μM ARB on intracellular ATP levels (n = 5 per group). (M) Effect of 75 μM ARB on mtDNA (n = 3 per group). (N–O) Mitochondrial membrane potential and its quantification (n = 4 per group). (P–Q) ROS staining with Mitosox red probe and its quantification (n = 3 per group). (R–S) Effect of 75 μM ARB on intracellular GSH and SOD content (R: n = 3 per group, S: n = 4 per group). (T–V) Effect of 75 μM ARB on intracellular Fe, Fe2+ and the ratio of Fe2+ to Fe3+ (n = 3 per group). (W) Calcein staining and its quantification (n = 3–4 per group). (X) qPT-PCR of ferroptosis-related genes (n = 3–4 per group). (Y–Z) Western Blot detects the protein expression levels of GPX4 and SLC7A11 under ARB treatment (n = 3 per group). Data are mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3; The data between two groups were analyzed by independent samples t-test, and one-way ANOVA was used to compare the means of three groups, ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)