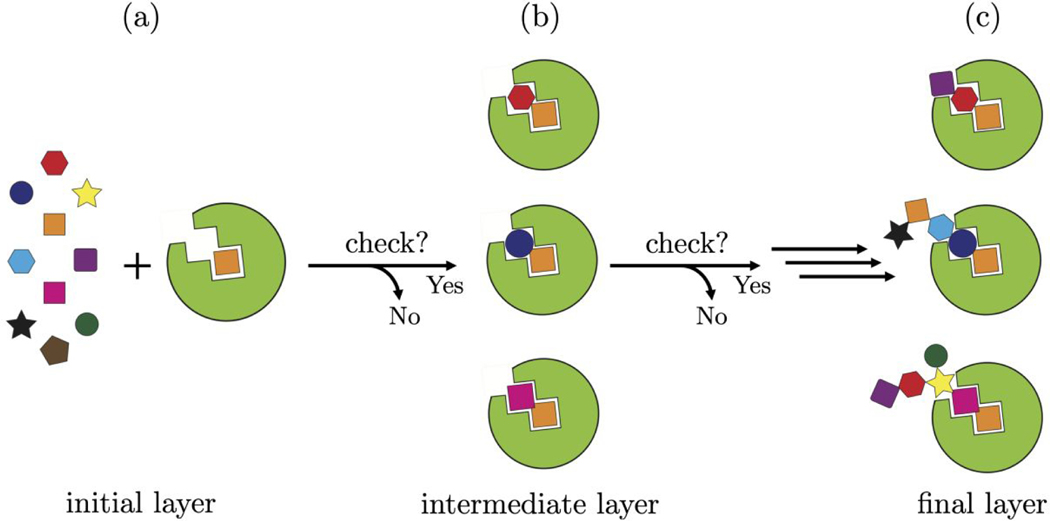
Figure 1.
Schematic outlining showing the D3N algorithm. (1a) An anchor (initial layer, orange square) is selected from the fragment library (colored fragments) and oriented/scored in the protein binding site (green). (1b) As candidate fragments are added to the anchor, the partially grown molecules must conform to the user-defined descriptor ranges (intermediate layer, orange + colored fragment) or the fragment is rejected. The process continues until the desired number of layers is reached (the present work employed up to 9 layers of growth). (1c) The final ensemble will be enriched with fully grown molecules (multi-colored and connected fragments) that conform to the user-defined descriptor ranges.