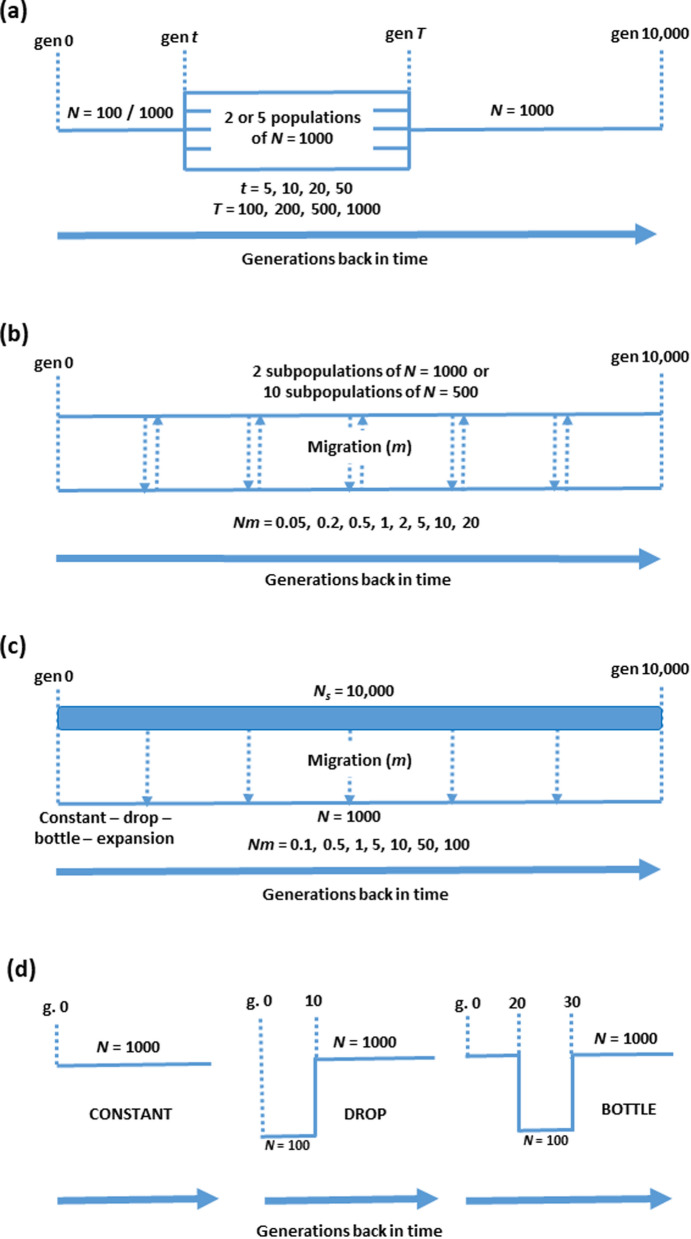
Fig. 1.
Population scenarios considered. a A synthetic population of size N individuals was generated t generation ago by the mixture of two or five populations of size N = 1000 individuals, which diverged T generations ago from an ancestral population (t < T). b A population subdivided into two or ten subpopulations was run with continuous migration between them with a reciprocal migration rate m per generation. c A population with N = 1000 individuals was maintained and received migrants from a larger source population of size Ns = 10,000 individuals at a rate m per generation. The recipient population was either kept at a constant population size, or suffered from a recent decline in size, a recent population bottleneck and recovery, or an expansion. d A closed population was run in which individuals carried a large chromosomal inversion. The population was either kept at a constant size or was subjected to a recent drastic drop, or a bottleneck and later recovering the previous size. Generation 0 is the current one, and generations are shown back in time in all cases