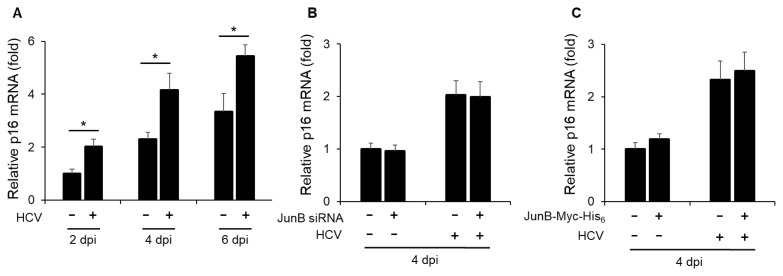
Fig. 4. JunB is not involved in the HCV-induced enhancement of p16 mRNA levels.
(A) Huh-7.5 cells were infected with HCV J6/JFH1 at an MOI of 1. At 2, 4, and 6 dpi, the cells were harvested, the total RNA was extracted, and mRNA levels of p16 were quantitated by real-time RT-PCR. Amounts of intracellular p16 mRNA were normalized to amounts of GAPDH mRNA. Data represent means ± SEM of data from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared with the controls. (B) Huh-7.5 cells were transfected with 40 nM JunB siRNA or control siRNA. At 24 h post-transfection, cells were infected with HCV J6/JFH1 at an MOI of 1. At 4 dpi, the cells were harvested. The total RNA was extracted and mRNA levels of p16 were quantitated by real-time RT-PCR. (C) Huh-7.5 cells were infected with HCV J6/JFH1 at an MOI of 1. At 3 h postinfection, cells were transfected with either pEF1A-JunB-Myc-His6 or pEF1A-Myc-His6. At 4 dpi, the cells were harvested. The total RNA was extracted and mRNA levels of p16 were quantitated by real-time RT-PCR.