Fig. 2B (original panel).
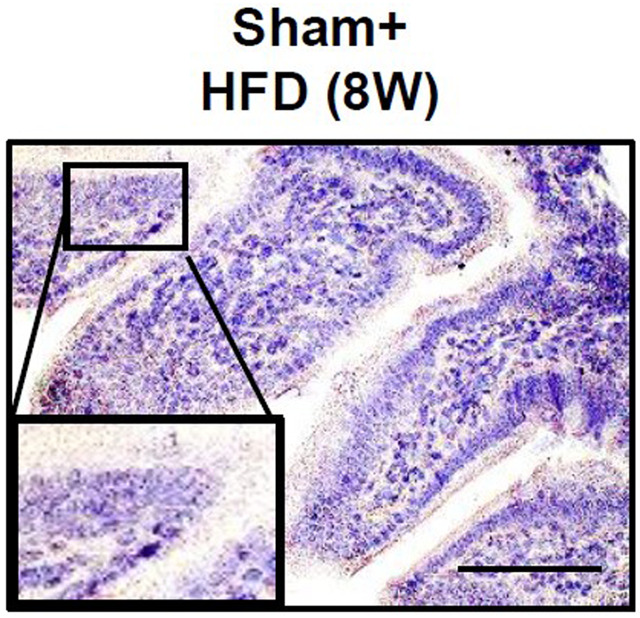
Effect of autonomic neural signal transduction on the tight junction in the small intestine of NAFLD/NASH mice models. (A,B) Representative images of Claudin-1 (A) and Zo-1 (B) staining of the small intestine of mice groups.
Fig. 2B (corrected panel).
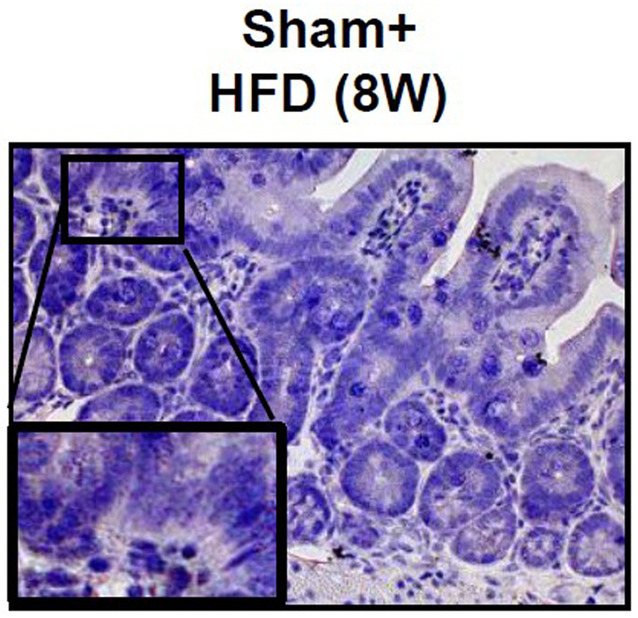
Effect of autonomic neural signal transduction on the tight junction in the small intestine of NAFLD/NASH mice models. (A,B) Representative images of Claudin-1 (A) and Zo-1 (B) staining of the small intestine of mice groups.
There was an error in Dis. Model. Mech. (2021) 14, dmm048922 (doi:10.1242/dmm.048922).
An incorrect image was used for Sham+HFD (8W) in Fig. 2B. The original and corrected versions are shown below.
The online full text and PDF versions of the paper have been corrected. The authors apologise to readers for this error, which does not impact the results or conclusions of the paper.


