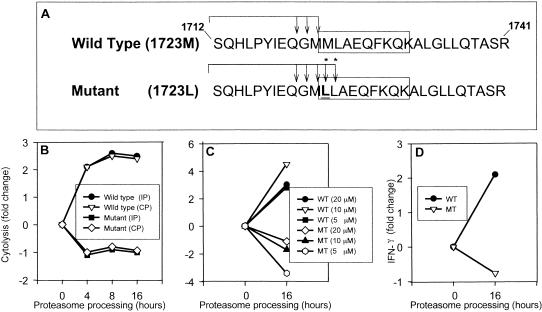
FIG. 5.
Proteasome processing of synthetic NS4B peptides. (A) Two synthetic peptides spanning amino acids S1712 to R1741 of NS4B containing either the HCV-1 wild-type (M1723) or mutant (L1723) sequences were synthesized and purified by RP-HPLC. NS4B1723 epitopes are boxed. Both peptides were processed with the constitutive proteasomes (CP) or immunoproteasomes (IP) for 16 h and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry was used to identify fragments. Fragments generated by cleavage of peptide bonds immediately before or after the NH2 terminus of the wild-type (WT) and mutant (MT) epitopes are shown. Asterisks indicate unique cleavage sites detected only in the peptide with M1723L substitution by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. (B) Wild-type peptide or peptides with M1723L substitution were mock digested in buffer alone (0 h) or buffer containing constitutive proteosomes or immunoproteasomes for 4, 8, or 16 h. Aliquots of the processed peptides (equivalent to approximately 60 μM of the wild-type or mutant substrate) were used to sensitize target cells for lysis by the NS4B1723-specific CTL line. CTL activity was measured at a 20:1 E:T ratio in a 4-h assay. The percentage of specific lysis of target cells sensitized with the mock-digested wild-type or mutant peptides was normalized to 0, and the fold increase or decrease in cytolytic activity with the immunoproteasome-digested peptides was calculated. The percentages of lysis of targets sensitized with mock-digested wild-type and mutant polypeptides were 20 and 35%, respectively. Four percent lysis was detected against unsensitized targets. (C) Wild-type peptides or peptides with M1723L substitution were processed with the immunoproteasome for 16 h as described above, and serial dilutions of the product, equivalent to 20, 10, and 5 μM concentrations of the starting substrate, were used to sensitize target cells. The fold change in cytolytic activity after immunoproteasome treatment was calculated as described above. The percentages of lysis of targets treated with mock-digested wild-type and mutant polypeptide were 22 and 50%, respectively. (D) Wild-type or mutant NS4b1723 peptides were mock digested or treated with the immunoproteasome for 16 h. BLCL cells sensitized with the processed products were cocultured with the NS4B1723-specific CTL line. The frequency of T cells producing IFN-γ was measured by flow cytometry.