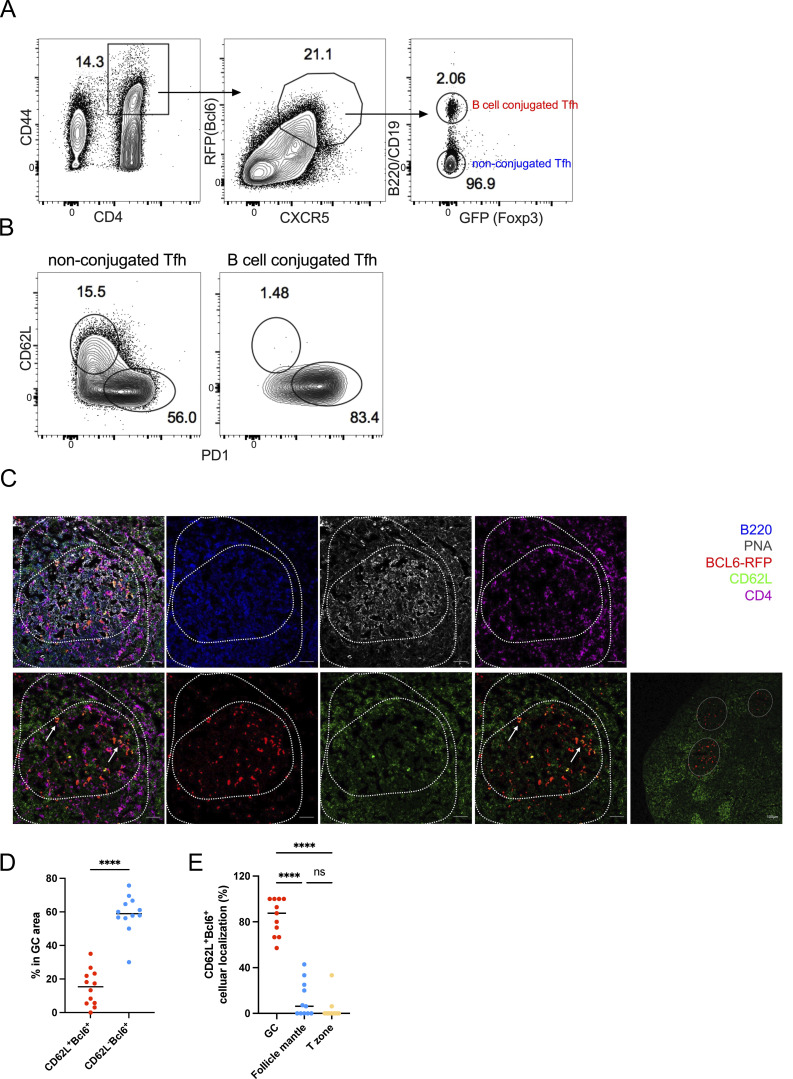
Figure 4.
CD62L-expressing Tfh cells are not in contact with B cells, and prone to circulate. (A) The gating strategy used for isolating B cell–conjugated GC-Tfh cells. Cells were obtained from the draining lymph nodes of Bcl6RFPxFoxp3GFP double reporter mouse on day 8 after KLH immunization. (B) Representative flow cytometry staining of PD-1 and CD62L expression on B cell–conjugated and unconjugated Tfh cells after EDTA treatment. (C–E) BCL6-RFP reporter mice were subcutaneously immunized with KLH, and the draining lymph nodes were isolated, embedded in OCT, and subjected to cryosectioning for subsequent immunofluorescence staining. (C) Representative immunofluorescence staining of B220 (blue), PNA (gray), BCL6-RFP (red), CD62L (green), and CD4 (violet), and multicolor overlapping images of the frozen sections. The upper panels represent five-color overlapping, B220, PNA, and CD4 staining (left to right); the bottom panels represent three-color overlapping (CD62L+Bcl6−RFP+CD4), Bcl6−RFP, CD62L, two-color overlapping (CD62L+Bcl6−RFP) of single GC, and entire follicles (left to right). White arrows indicate CD62L+BCL6-RFP+ CD4 T cells in the GC area. The length of scale bars represents 50 µm, unless labeled in the image. (D) Statistical analysis of CD62L+BCL6-RFP+ and CD62L−BCL6-RFP+ CD4 T cells in GC areas. (E) Statistical analysis of CD62L+BCL6-RFP+ CD4 T cells localized in GC area (PNA+B220low), follicle mantle (PNA−B220+), and T cell zone (PNA−B220−CD4+). Data of A–E represent two independent experiments. Data are shown as mean. Paired t test; ****, P < 0.0001, ns, no significance.