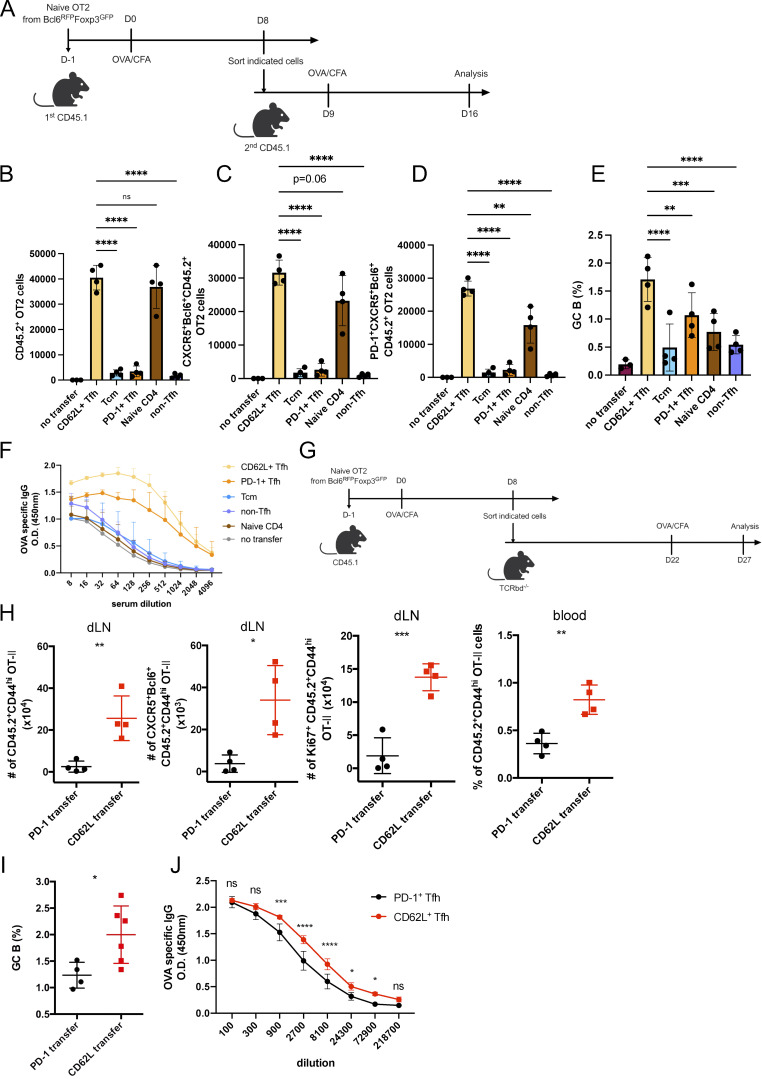
Figure S4.
CD62L-expressing Tfh cells promote recall responses. (A) Schematic diagram of adoptive transfer with indicated T cell populations and OVA immunization. (B–D) Absolute numbers of (B) CD45.2+OT-II+CD4+ T cells, (C) CD45.2+OT-II+ CD4+CXCR5+Bcl6+ Tfh cells, (D) PD-1+CD45.2+OT-II+ CD4+CXCR5+Bcl6+ Tfh cells, in mice adoptively transferred with indicated cells on day 7 after OVA immunization. (E) Statistical analysis of GC B cell percentages of mice receiving indicated cells. (F) OVA-specific IgG levels in sera of mice receiving indicated cells were measured by ELISA. (G) Schematic diagram of PD-1+ or CD62L+ Tfh cell adoptive transfer experiment with OVA immunization. (H) Absolute numbers of CD45.2+ OT-II T cells, CD45.2+ CD4+CXCR5+Bcl6+ OT-II Tfh cells, or Ki67+ CD45.2+ OT-II T cells in draining lymph nodes or circulating blood from recipient mice adoptively transferred with PD-1+ or CD62L+ Tfh cells on day 5 after OVA reimmunization. (I) GC B cell percentages in draining lymph nodes from recipient mice were adoptively transferred with PD-1+ or CD62L+ Tfh cells on day 5 after OVA reimmunization. (J) Antigen-specific IgG level in serum from recipient mice receiving PD-1+ or CD62L+ Tfh cells. Data above are representative of two independent experiments. Data of A–J represent two independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± SD; two-tailed t test; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, no significance.